

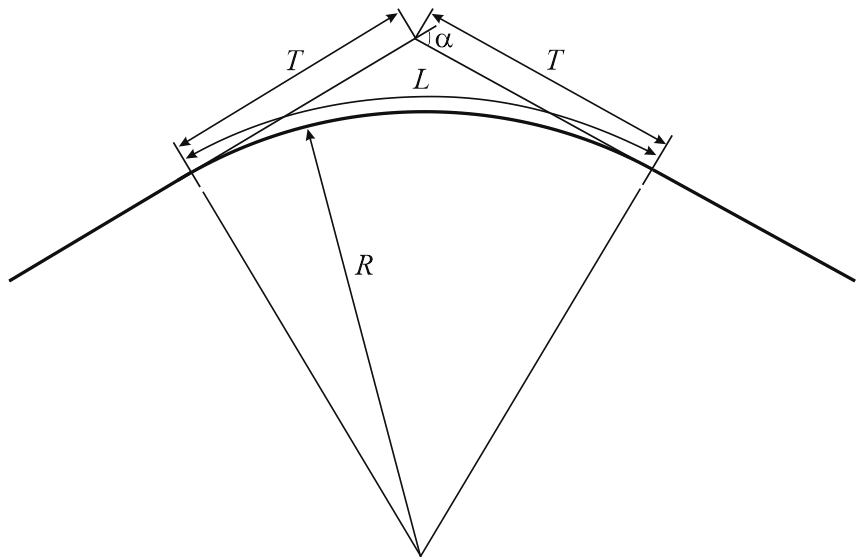
Elastic bends form when straight pipe sections bend during field installation. Bend radius typically exceeds 10×DN. Unlike factory-fabricated bends, elastic bends contain initial bending stresses from installation deformation. Maximum bend angle should not exceed 90° (details).
Factory-fabricated long-radius bends maintain their curved shape without external forces (Fig. 1a). Elastic bends start as straight pipe segments (Fig. 1b) that deform during installation (Fig. 1c). Removing external forces returns elastic bends to straight configuration (Fig. 1d).
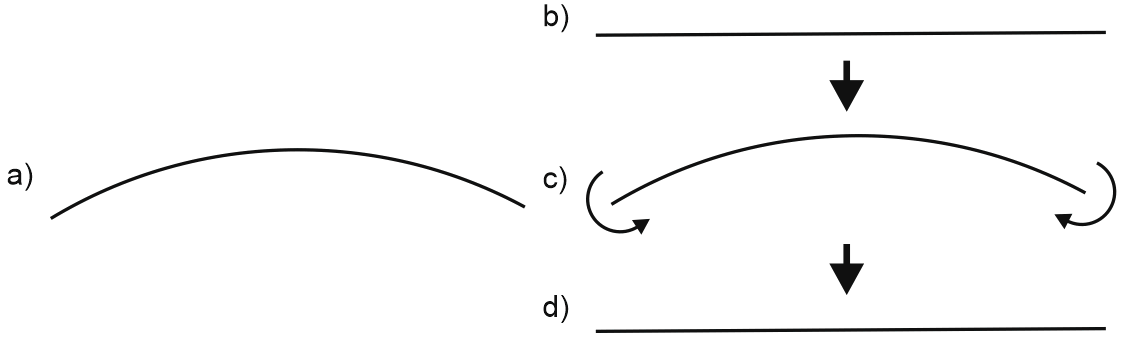
Fig. 1. Factory bend vs. elastic bend behavior
PASS/START-PROF performs additional longitudinal stability analysis for elastic bends. In START-Base, automatic stability checks generate error messages for insufficient stability in the errors and warnings window. Additional stability verification available via START-Elements bend stability analysis.

Property |
Description |
Radius, R |
Bend radius (R > 10×D) |
Curve Length, L |
Arc length of bend |
Tangent, T |
Bend tangent length |
Get Properties from Matching Pipe |
Import properties from adjacent pipe element |
Material |
Material selection from materials database |
Nominal Wall Thickness, S |
Nominal (as-built) wall thickness |
Mill Tolerance |
Manufacturing thickness tolerance. Details... |
Corrosion Allowance |
Wall thickness allowance for corrosion and erosion. Details... |
Calculate Weight Automatically |
Automatic weight calculation using:
Material density from database |
Design Factor, Df |
Design factor per ASME NM.1 Table 2-3.2.2-2 |
Design Factor, DFt |
Test mode design factor (default: 1.0) |
Type |
Laminate type specification |
Pipe Linear Weight |
|
Insulation Linear Weight |
|
Content Linear Weight |
Insert elastic bend by selecting target node and using: Insert > Bend > Elastic Bend
View existing element properties:
Double-click element in 3D view
Select element and click  toolbar icon
toolbar icon