SNIP 2.05.06-85: 95% of
specified yield strength σ = 0.95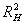
RD 10-249-98 (Tables 2,8):
σ = 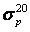 /1.1 ≈ 0.9
/1.1 ≈ 0.9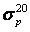
PB 03-585-03 [1]: 90%
of yield strength at test pressure: σ = 0.9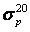
Learn more about PASS/START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
Required nominal wall thickness calculation:
S ≥ SR + С
Where:
SR - Design wall thickness (minimum required for internal pressure per applicable codes)
С - Total wall thickness allowance
Total allowance C calculation:
С = С1 + С2
Where:
С1 - Manufacturing allowance (mill tolerance), combining negative wall thickness deviation C11 and manufacturing process tolerance C12. ASME codes use percentage values; Russian codes use millimeters.
С11 - Negative tolerance compensation allowance. Defined by code or specification requirements. Excludes design thickness rounding to standard values.
С12 - Manufacturing process allowance for wall thinning during forming operations (stretching, pressing, bending). Determined by fitting manufacturing specifications.
С2 - Corrosion and erosion allowance. Determined by design codes or industry standards based on projected service life. Increase for double-sided corrosion exposure.
Nominal wall thickness S must meet minimum values specified in applicable codes and round up to standard thickness values.
During input data validation, PASS/START-PROF verifies wall thickness adequacy for design pressure using:
S - C ≥ SR
Nominal thickness S and total allowance C are defined in element properties. Minimum design thickness SR follows code requirements selected in Project Settings.
ASME code verification applies to straight pipes and bends only. Other fittings are excluded from wall thickness checks.
When factory test pressure values are insufficient, system must withstand hydraulic testing to pressures producing equivalent stresses of:
SNIP 2.05.06-85: 95% of
specified yield strength σ = 0.95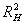
RD 10-249-98 (Tables 2,8):
σ = 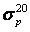 /1.1 ≈ 0.9
/1.1 ≈ 0.9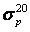
PB 03-585-03 [1]: 90%
of yield strength at test pressure: σ = 0.9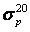
PASS/START-PROF performs test pressure wall thickness verification using (GOST 32388-2013 sustained condition only):
S ≥ ST
ST - Minimum wall thickness for test pressure per Project Settings codes. Test temperature Тtest defined in Project Settings, test pressure Ptest in element properties, material yield strength in materials database.
Per GOST 8731 and GOST 8733, carbon and low-alloy seamless pipes must withstand
hydraulic pressure at 40% of tensile strength: σ = 0.4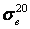 ,
which may not satisfy code requirements.
,
which may not satisfy code requirements.
Pipes satisfy GOST 8731 and GOST 8733 only when:
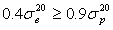
Example
- Steel 20: According to [2], tensile strength
at 20°C 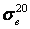 = 460 MPa, yield strength
= 460 MPa, yield strength 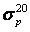 = 250 MPa. Condition evaluation:
= 250 MPa. Condition evaluation:
0.4 ∙ 460 < 0.9 ∙ 250 MPa
or
184 < 225 MPa
Condition not satisfied. Standard test pressure requirements are not met, requiring stricter factory testing at 225 MPa pressure (GOST documents include relevant notes).
Reinforced wall thickness calculation:
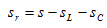
Where:
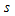 - Nominal
wall thickness
- Nominal
wall thickness
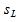 - Internal
protective layer thickness
- Internal
protective layer thickness
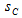 - External
protective layer thickness
- External
protective layer thickness
1. PB 03-585-03, Rules for Design and Safe Operation of Process Piping, Moscow, 2003
2. GOST 34233.1-2017 Boiler and Pressure Vessels Code