

Learn about START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
START-PROF automatically considers the following for nozzles:
Analysis results are available in the Loads on Nozzles and Equipment Table. See also "How to Reduce Nozzle Loads in START-PROF"
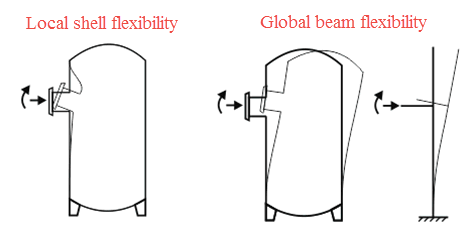
The flexibility at the vessel-pipe junction consists of two components: local flexibility and global flexibility. Local flexibility accounts for shell deformation near the nozzle, while global flexibility considers vessel bending behavior.
Nozzle elements model pipe connections to pressure vessels and columns. Three modeling approaches are available:
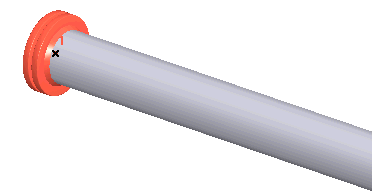
1. Nozzle element at end node. Global flexibility is excluded unless calculated using Nozzle-FEM software. Thermal expansion effects are automatically modeled.
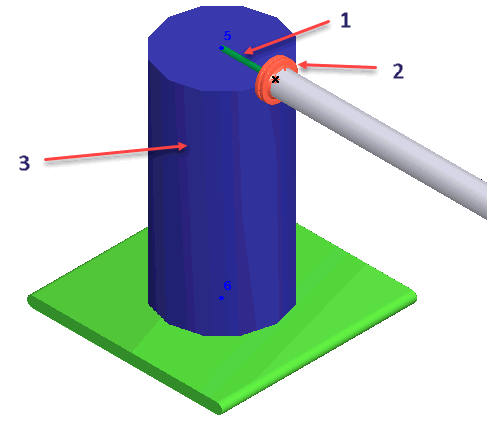
2. Vessel modeled using cylindrical shell element (3). Distance between nozzle and vessel axis intersection point modeled with rigid element (1). Nozzle element placed between pipe and rigid element (2). This method accommodates complex equipment configurations with multiple pipe connections and considers both local and global flexibility. Thermal expansion effects are included through shell and rigid element properties.
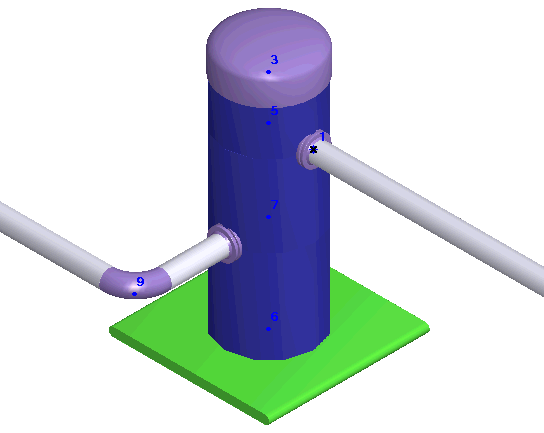
3. Vessel modeled using cylindrical shell element. Nozzle element inserted at pipe axis-cylindrical shell intersection point as a standard tee (node 1). START-PROF automatically generates the rigid element. Both local and global flexibility are considered.
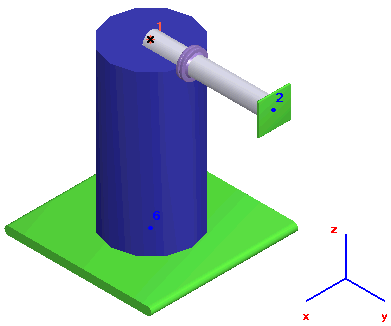
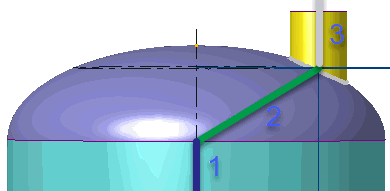
4. For dish end connections, connect the rigid element (2) to the cylindrical shell element end (1) and nozzle junction point (3).

Property |
Description |
Name |
Element identifier. Elements can be sorted by name and selected in the project tree |
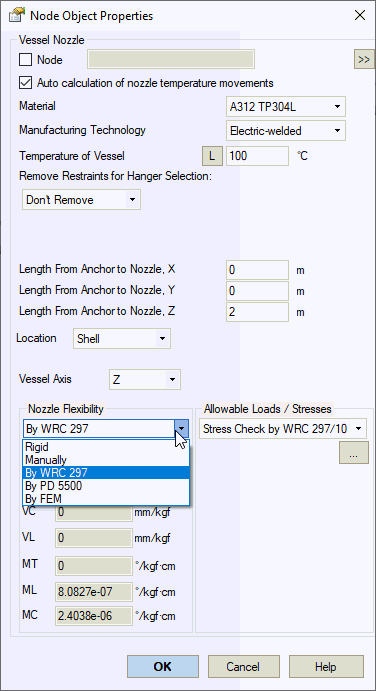
Auto calculation of nozzle temperature movements |
Automatically calculates nozzle movements as ΔX=α(T-Ta)·DX, where α is thermal expansion coefficient from material properties, T is equipment temperature, Ta is ambient temperature, and DX, DY, DZ are user-specified distances from anchor point to nozzle. When disabled, nozzle movements can be specified manually. |
Material of Vessel |
Material selection from materials database |
Manufacturing technology of Vessel |
For ASME B31.3, DL/T 5366-2014: seamless pipe uses Wl=1.0, electric-welded pipe uses database values. More... For GOST 32388-2013, material properties vary by pipe type (seamless/welded) from materials database. |
Temperature of Vessel, Top |
Design temperature in operating mode. More... This property can be modified in different operating
modes. Click |
Remove restraints for hanger selection |
When enabled, specific restraints are temporarily removed from nozzle elements during variable and constant spring selection weight analysis. Restraints remain active during primary analysis. This approach isolates weight loading from nozzle elements, allowing springs to support loads where pure weight displacements equal zero. Options:
|
Internal diameter of vessel |
Vessel internal diameter |
Length from anchor to nozzle X,Y,Z |
Distance between vessel anchor point and nozzle. Used for modeling nozzle thermal expansion movements. Applies only to end node nozzles. Movement along each axis: ΔX=α(Tope-Tambient)LX. Thermal expansion coefficient obtained from material database.
|
Location |
Nozzle attachment location: bottom (cap) or shell |
Node lying on the axis |
For off-center bottom nozzles, specify any node on vessel axis to create local coordinate system. Leave blank for centered bottom nozzles. |
Nozzle flexibility |
Flexibility calculation methods:
Nozzle-shell junction coordinate system: P - Nozzle axis (Xm) VL - Perpendicular to P, in plane containing P axis and vessel axis VC - Perpendicular to P and VL MT - Rotation around P ML - Rotation around VC MC - Rotation around VL
Inclined nozzle to head junction: P - Nozzle axis (Xm) VL - Perpendicular to P, in plane containing P axis and vessel axis VC - Perpendicular to P and VL Offset nozzle to head junction: P - Nozzle axis (Xm) VL - Perpendicular to P, in plane containing P axis and head center node VC - Perpendicular to P and VL Central nozzle to head junction: P - Nozzle axis (Xm) VL - Along vessel Zm axis (see global and local coordinate system) VC - Along vessel Ym axis
|
Don't Exclude the Beam Flexibility |
When disabled, only local shell flexibility is considered: λ = λs - λb When enabled, both local shell and global beam flexibilities are considered: λ = λs λs - flexibility from finite element shell model, λb - flexibility from equivalent beam model. Refer to PASS/Nozzle-FEM user's guide
|
Allowable loads / stresses |
Verification methods:
|
To insert a nozzle: select target node and use Insert > Equipment > Vessel Nozzle