

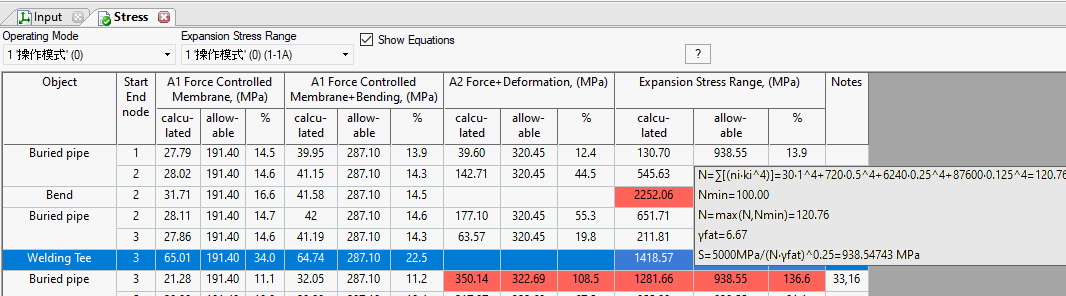
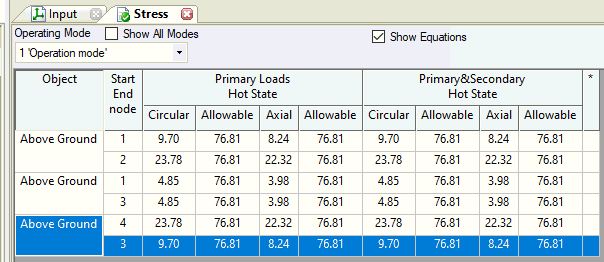
The piping stress table displays results for load cases required by the selected design code.
Stress table format varies based on the code selected in Project Settings and analysis mode:
Stress from seismic wave propagation effect are described here
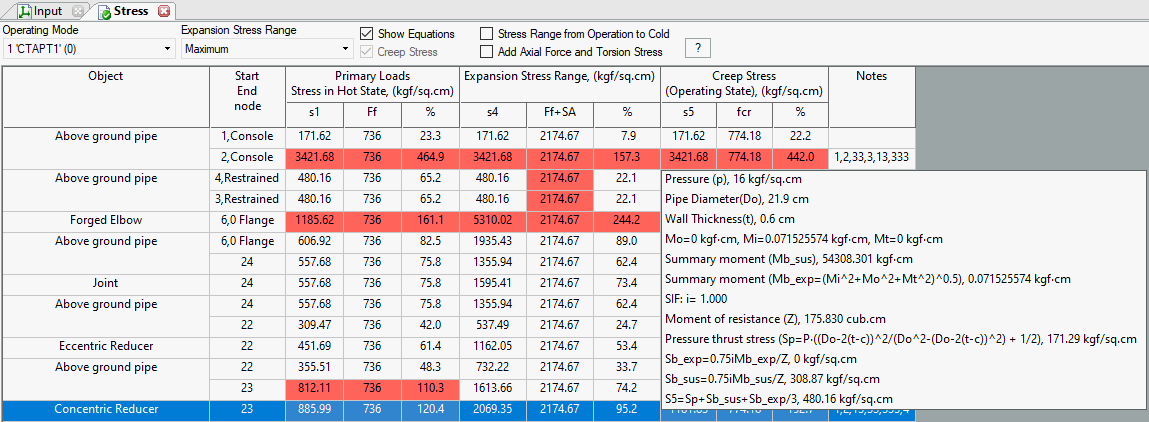
View stresses for a specific operating mode or the maximum stress across all modes. Selecting "Maximum" displays the highest stress ratio (calculated stress divided by allowable stress) for each table cell, along with its corresponding allowable stress.
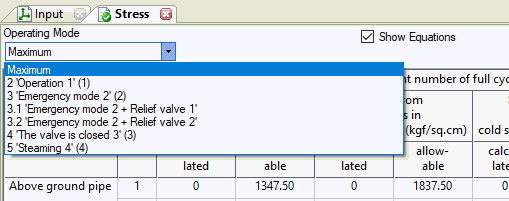
Stress is calculated for straight pipes (at start and end nodes), bends (at start and end nodes), and tees (in three cross-sections). See the "internal forces in piping elements" section. For accurate analysis, divide long buried sections (exceeding 150 diameters in length) by adding intermediate nodes. Also add intermediate nodes at mid-span between above-ground pipeline supports for more precise stress calculation.
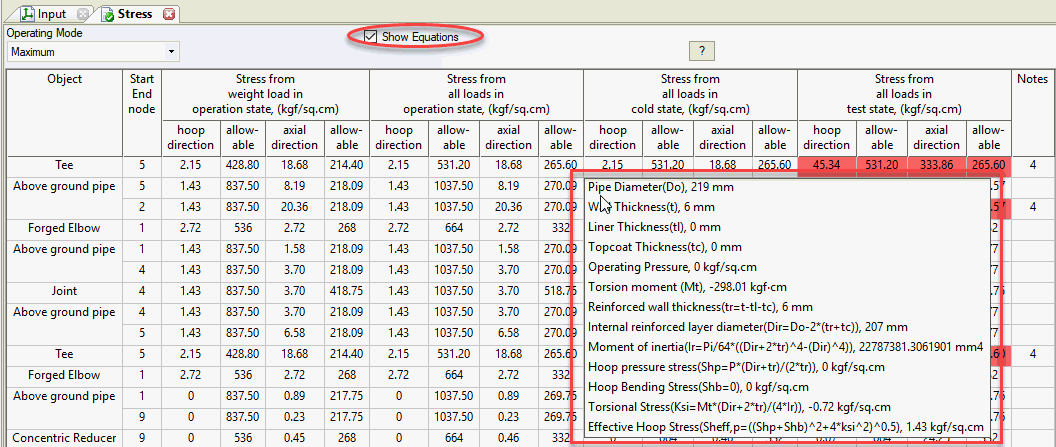
Check "Show Equations" to view calculation formulas. Hover over any table cell to see a popup with all equations used. Press CTRL+C to copy this text.
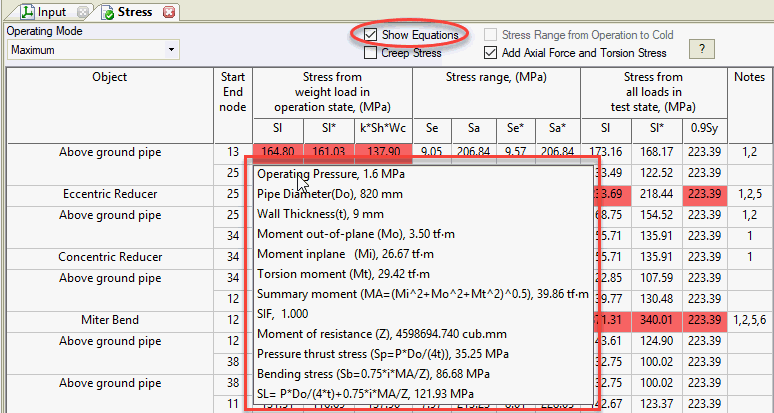
Cells failing strength requirements highlight in red, and the last column displays an error code. Hover over the code to read the message (see fig. below). Printed reports list errors and warnings below the table. If all requirements are met, the "notes" column remains empty.
Cells with the highest stress ratio (actual to allowable) highlight in yellow.
Primary Loads are force-driven (weight, pressure, spring preload). They are not self-limiting. Plastic deformation from primary loads continues until force equilibrium is reached. Excessive primary load causes gross deformation and rupture. Failure can occur in a single load application.
Secondary Loads and Expansion Stress. Secondary loads are displacement-driven (thermal expansion, anchor movement, settlement). They are self-limiting—stresses relieve through system yielding or deflection. Secondary loads are typically cyclic (except settlement). Allowable limits consider fatigue failure modes and are based on elastic shakedown and material fatigue curves. A single application never causes failure. Catastrophic failure occurs after numerous cycles. Successful long-term operation does not verify proper secondary stress design.
Stress calculation depends on these settings:
"High Temperature" mode in Operation Mode Editor
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
"Use Wc factors" in Project Settings
Corrosion allowance and mill tolerance do not affect stress calculations in this code.
Button |
Property |
Description |
|
Sustained/Occasional Stress, Sl |
A - cross-sectional area, F - axial force, Mi - in-plane moment, Mo - out-of-plane moment, Mt - torsional moment, Z - section modulus L1 - sustained loads (W+P), L6 - operating loads (W+P+T), L11 - operating + occasional loads (W+P+T+OCC) |
Allowable Sustained/Occasional Stress |
ASME B31.1 Sustained:
ASME B31.1 Occasional:
ASME B31.9 Sustained:
ASME B31.9 Occasional:
k - occasional load factor Sh - hot allowable stress from material database Wc - circumferential weld strength reduction factor from material database. Applies when "Use Wc factors" is enabled in Project Settings E - Weld Joint Efficiency Factor |
|
|
Stress Range, Se (operating to installation/cold) |
Calculated between operating and installation modes. Uses operating to cold mode if "stress range from operation to cold" is enabled.
ASME B31.1 buried piping includes additional straight pipe check per VII-4.5, VII-5:
|
Allowable Stress Range, Sa |
N - total cycles, calculated by:
Cycle data from temperature cycles Buried straight pipes allowable stress:
|
|
|
Test Condition Sustained Stress, Sl |
Same as sustained/occasional stress calculation |
Allowable Test Condition Stress |
|
|
|
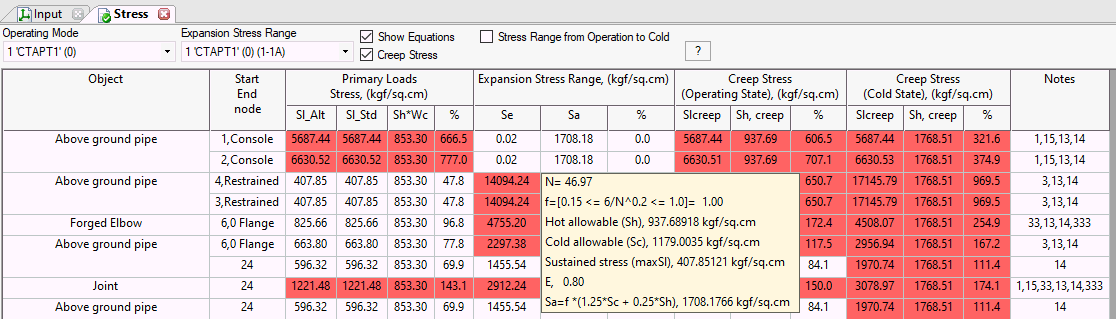
Operating Creep Stress (sustained + displacement) |
Active only when "Consider creep effect" is enabled in Project Settings Calculated similar to Sl and Sl*, with temperature difference multiplied by "creep diminish factor" from pipe properties |
Allowable Stress |
Sh - hot allowable stress |
|
|
Cold Condition Creep Stress (sustained + displacement) |
Active only when "Consider creep effect" is enabled in Project Settings Calculated similar to Sl, with temperature difference multiplied by "creep self-springing factor" from pipe properties |
Allowable Stress |
1.5Sc - cold allowable stress |
Stress calculations depend on the following settings:
"High Temperature" mode in the Operation Mode Editor
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
"Use Wc factors" enabled in Project Settings
"Maximum f always 1.0" in Project Settings
High Pressure Piping designation in Pipe Properties
For sustained stress calculations, the cross-sectional area (A) and section modulus (Z) are reduced by the corrosion allowance.
For displacement stress calculations, the cross-sectional area (A) and section modulus (Z) are not reduced.
Button |
Property |
Description |
|
Stress due to sustained or occasional loads, SL |
Occasional stress:
A - cross-sectional area, F - axial force, Mi - in-plane moment, Mo - out-of-plane moment, Mt - torsional moment, Z - section modulus L1 - sustained loads (W+P), L6 - operating loads (W+P+T), L11 - operating loads + occasional force-based loads (W+P+T+OCC) ASME B31.3 defines two sustained stress types: SL_Alt and SL_Std SL_Std - Sustained stress at cold condition (W+P). Includes unidirectional restraints and gap element states. Typically, all rigid supports are active. SL_Alt - Sustained stress at hot condition (W+P). Uses the same restraint and gap configuration as the operating state (W+P+T). Some rigid supports may be inactive due to lift-off. If no supports lift off in the hot operating mode (W+P+T), SL_CLD and SL_HOT are equal. |
Allowable stress for sustained or occasional loads |
Sustained:
Occasional:
k - occasional load factor Sh - hot allowable stress from material database Sy - yield stress from material database Wc - circumferential weld strength reduction factor from material database. Applied when "Use Wc factors" is enabled in Project Settings |
|
|
Stress range between operating and (installation/cold) state, SE |
Stress range calculated between operating and installation conditions. When "stress range from operation to cold" is enabled, calculated between operating and cold conditions.
|
Allowable stress range, SA |
N - number of full equivalent cycles. Calculated as:
Cycle data is obtained from temperature history |
|
|
Stress due to sustained loads in test condition, SL |
Same as stress due to sustained or occasional loads, SL |
Allowable stress for sustained loads in test condition |
|
|
|
Creep stress from sustained and displacement loads in operating mode |
Evaluated only when "Consider creep effect" is enabled in Project Settings Calculated similarly to SL, but temperature difference is multiplied by the "creep diminish factor" from pipe properties |
Allowable stress |
Sh - hot allowable stress |
|
|
Creep stress from sustained and displacement loads in cold condition |
Evaluated only when "Consider creep effect" is enabled in Project Settings Calculated similarly to SL, but temperature difference is multiplied by the "creep self-springing factor" from pipe properties |
Allowable stress |
1.5Sc - cold allowable stress |
|
|
Creep-Rupture Usage Factor, u |
Creep-Rupture Usage Factor, u per ASME B31.3-2018, V303.2
|
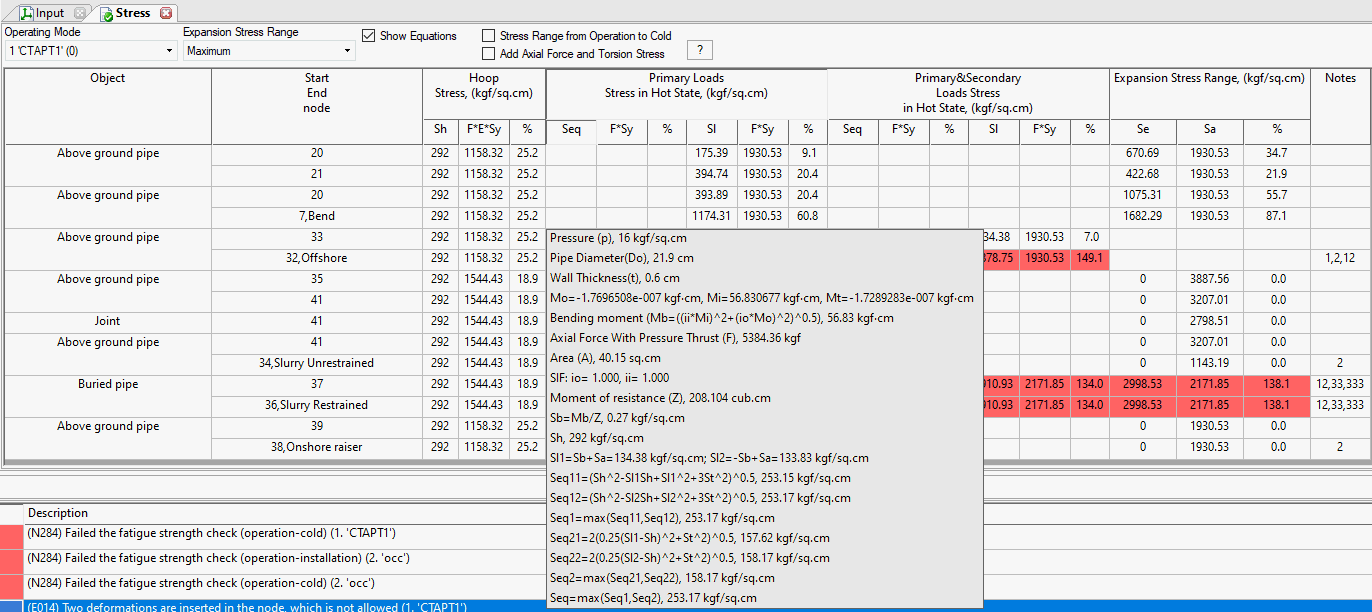
Stress calculations depend on the following settings:
"Add axial force and torsion stress" in Project Settings
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
Maximum distortion energy theory setting (True/False/Maximum) in Project Settings
Restrained/Unrestrained pipe designation: Manual, Autodetect, or START Smart Check in Project Settings
Pipeline location: Onshore Pipeline, Slurry Pipes, or Offshore Pipeline in Pipe Properties
Pipeline type: Restrained, Unrestrained, or Riser and Platform for Inland Waterways in Pipe Properties
Corrosion allowance does not affect stress calculations in this code.
Sustained, Operating, Expansion, and Test stresses:
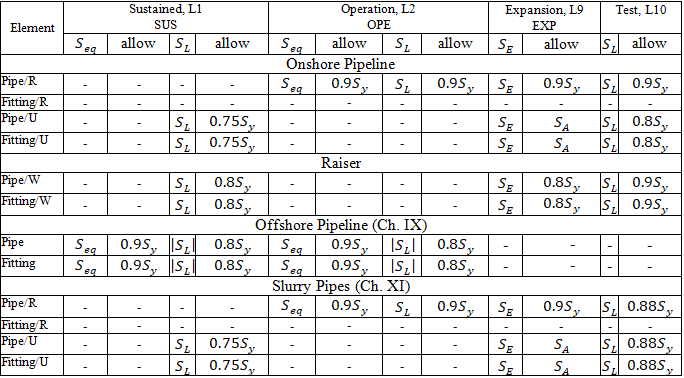
START Smart Check:
Stresses from occasional loads:
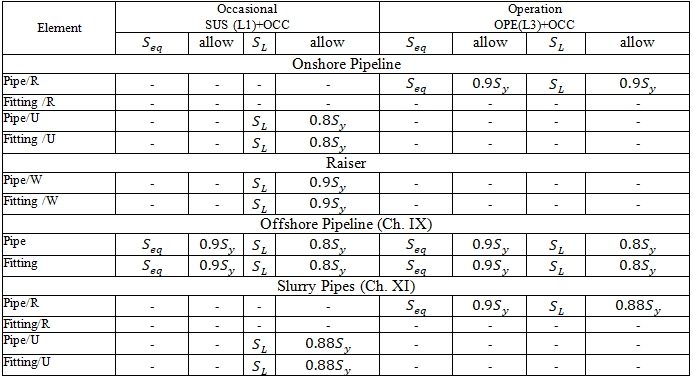
START Smart Check for occasional loads:
Stress calculations depend on the following settings:
"Add axial force and torsion stress" in Project Settings
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
For sustained stress calculations, the cross-sectional area (A) and section modulus (Z) are reduced by the corrosion allowance.
For displacement stress calculations, the cross-sectional area (A) and section modulus (Z) are not reduced.
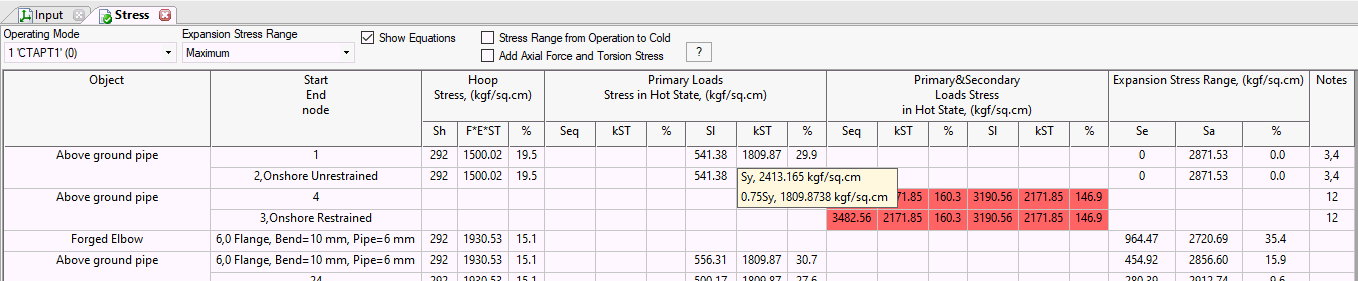
Stress calculations depend on the following settings:
"Add axial force and torsion stress" in Project Settings
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
Maximum distortion energy theory setting (True/False/Maximum) in Project Settings
Restrained/Unrestrained pipe designation: Manual, Autodetect, or START Smart Check in Project Settings
Pipeline location: Onshore Pipeline or Offshore Pipeline in Pipe Properties
Pipeline type: Restrained, Unrestrained, or Riser and Platform Piping in Pipe Properties
Corrosion allowance and mill tolerance do not affect stress calculations for all pipeline types except risers.
For risers, the cross-sectional area (A) and section modulus (Z) are reduced by corrosion allowance and mill tolerance.
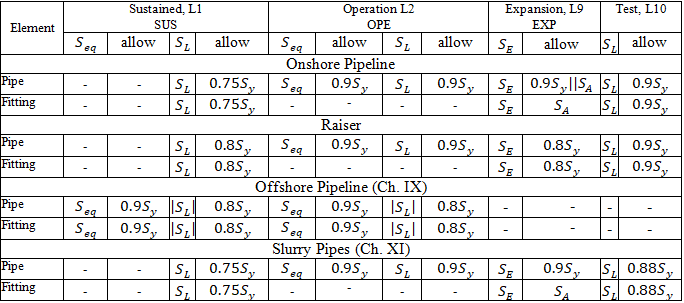
Sustained, Operating, Expansion, and Test stresses:
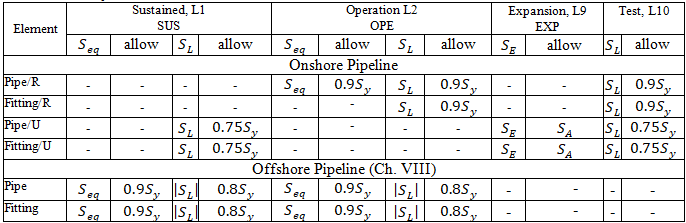
START Smart Check:
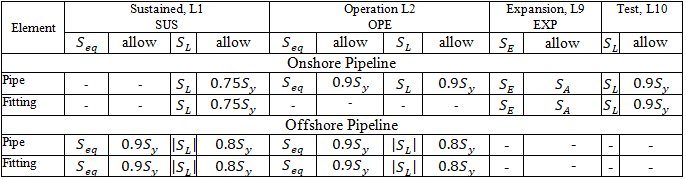
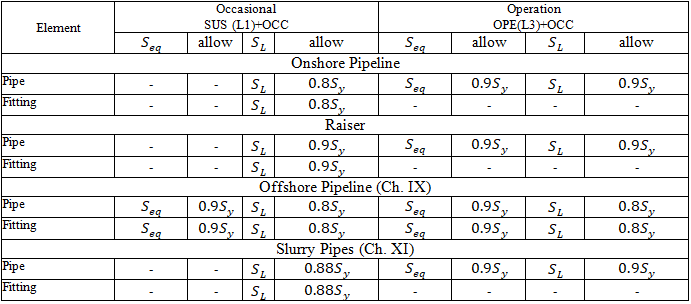
Stresses from occasional loads:
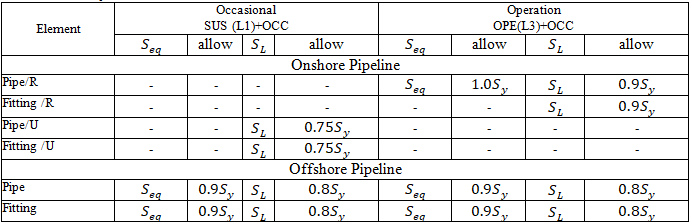
START Smart Check for occasional loads:
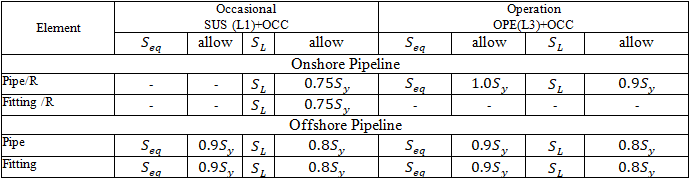
Stress calculations depend on the following settings:
"Add axial force and torsion stress" in Project Settings
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
Use In-plane/Out-plane SIF in Project Settings
Liberal Stress Allowable in Project Settings
With Surveillance of Creep Exhaustion in Project Settings
Consider Corrosion in Project Settings
When "Consider Corrosion" is disabled, corrosion allowance and mill tolerance do not affect stress calculations.
When "Consider Corrosion" is enabled, the cross-sectional area (A) and section modulus (Z) are reduced by the corrosion allowance for sustained and expansion stress calculations.
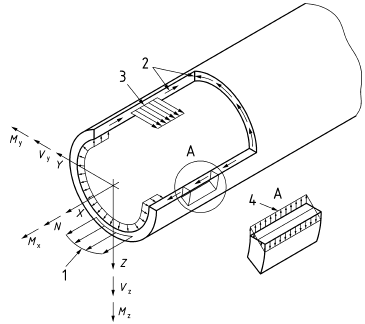
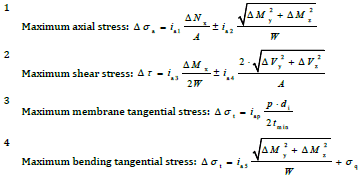
Button |
Property |
Description |
|
Force-controlled action LC2 Membrane Stress A1 |
|
Allowable stress |
|
|
|
Force-controlled action LC2 Membrane+Bending Stress A1 |
|
Allowable stress |
γm is specified in pipe properties |
|
|
Stepwise plastic deformation LC3 Force+deformation stress A2 |
|
Allowable stress |
|
|
|
Low
cycle fatigue |
|
Allowable stress |
ni - specified in temperature cycles and multiplied by service life from project settings. The equivalent number of full cycles must not be less than the minimum cycles Nmin specified in project settings, which depends on the pipeline type in pipe properties. Project class is specified in pipe properties.
|
Hover over any table cell to view a detailed report with equations and calculated values. Requires "show equations" option enabled.
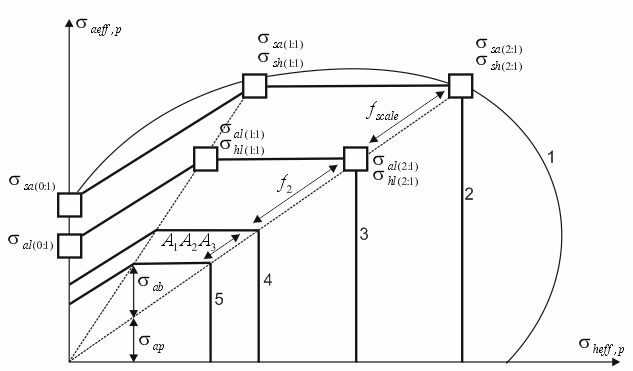
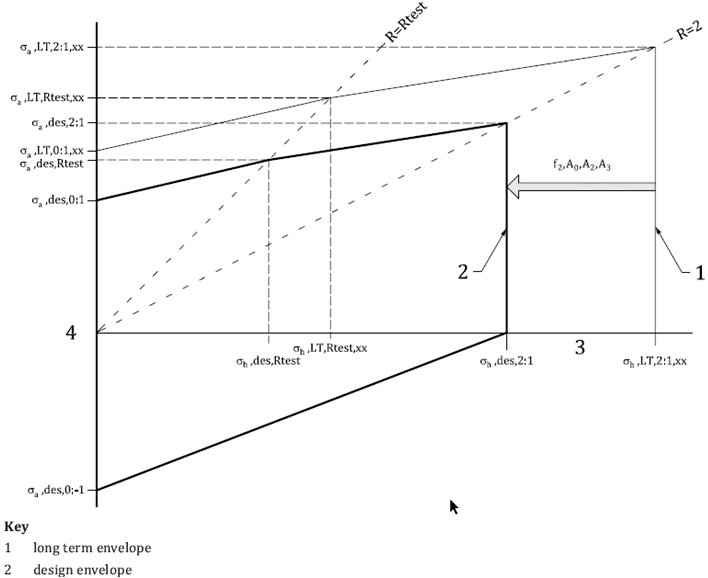
Full failure envelope
1 – Actual short-term failure envelope, 2 – Idealized short-term failure envelope, 3 – Idealized long-term failure envelope, 4 – Non-factored design failure envelope, 5 – Factored design long-term failure envelope
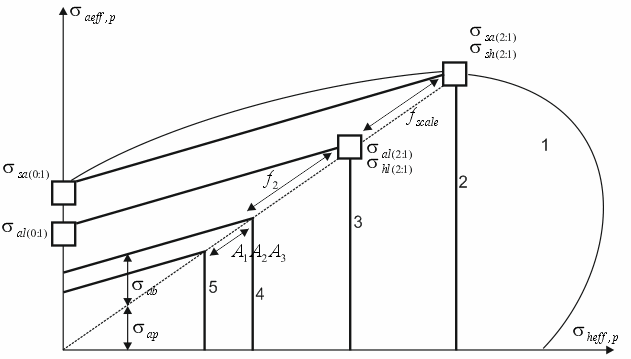
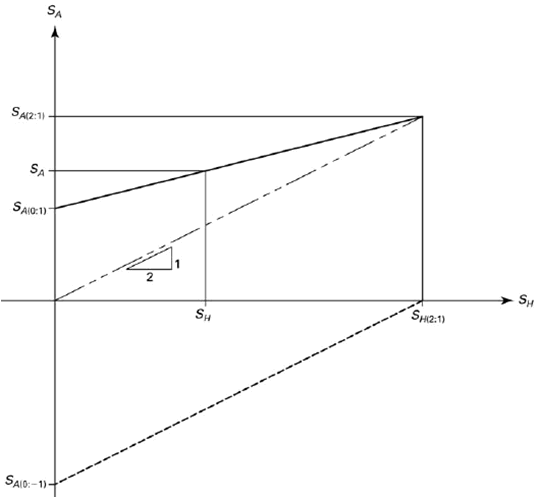
Simplified failure envelope
1 – Actual short-term failure envelope, 2 – Idealized short-term failure envelope, 3 – Idealized long-term failure envelope, 4 – Non-factored design failure envelope, 5 – Factored design long-term failure envelope
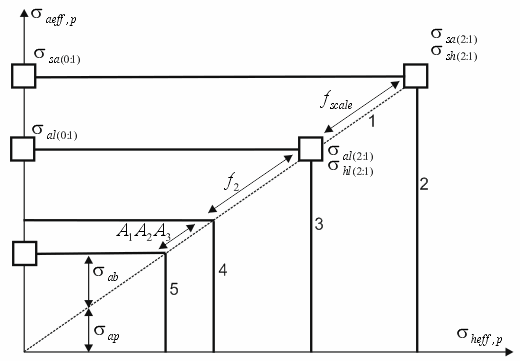
Simplified failure envelope for fittings and joints at r=1
1 – Stress to pressure correlation line (2:1), 3 – Idealized long-term failure envelope, 4 – Non-factored design failure envelope, 5 – Factored design long-term failure envelope
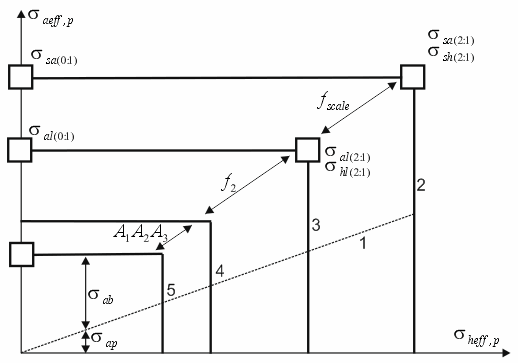
Simplified failure envelope for fittings and joints at r>1
1 – Stress to pressure correlation line (2:1), 3 – Idealized long-term failure curve, 4 – Non-factored design failure curve, 5 – Factored design long-term failure curve
Stress calculations depend on:
"Add axial force and torsion stress" in Project Settings
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
Button |
Property |
Description |
|
Stress due to sustained or occasional loads, SL |
Occasional stress:
Ap - cross-sectional area, F' - axial force with pressure thrust, Mi - in-plane moment, Mo - out-of-plane moment, Mt - torsional moment, Z - section modulus L1 - sustained loads (W+P), L6 - operating loads (W+P+T), L11 - operating loads + occasional force-based loads (W+P+T+OCC) |
Allowable stress for sustained or occasional loads |
Sustained:
Occasional:
k - occasional load factor S - allowable stress from material database |
|
|
Stress range between operating and (installation/cold) state, SE |
Stress range calculated between operating and installation conditions. When "stress range from operation to cold" is enabled, calculated between operating and cold conditions.
|
Allowable stress range, SA |
SA - from from material database |
|
|
Stress due to sustained loads in test condition, SL |
Same as stress due to sustained or occasional loads, SL |
Allowable stress for sustained loads in test condition |
|
Button |
Property |
Description |
|
Stress due to sustained or occasional loads, SL |
F' - axial force with pressure thrust, As - cross-sectional area, Zs - section modulus, Mi - in-plane moment, Mo - out-of-plane moment, Mt - torsional moment Occasional stress:
L1 - sustained loads (W+P), L6 - operating loads (W+P+T), L11 - operating loads + occasional force-based loads (W+P+T+OCC) |
Allowable stress for sustained or occasional loads |
Sustained:
Occasional:
k - occasional load factor |
|
|
Stress due to sustained loads in test condition, SL |
Same as stress due to sustained |
Allowable stress for sustained loads in test condition |
|
Stress calculations depend on:
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
"Maximum f always 1.0" in Project Settings
Corrosion allowance reduction of cross-sectional area (A) and section modulus (Z) for sustained stress calculations
Cross-sectional area (A) and section modulus (Z) are not reduced for displacement stress calculations.
Stress calculations depend on:
"Add axial force and torsion stress" in Project Settings
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
"Maximum f always 1.0" in Project Settings
Maximum distortion energy theory setting (True/False/Maximum) in Project Settings
Restrained/Unrestrained pipe designation: Manual, Autodetect, or START Smart Check in Project Settings
Pipeline type: Restrained or Unrestrained in Pipe Properties
Corrosion allowance and mill tolerance do not affect stresses except for risers.
For risers, cross-sectional area (A) and section modulus (Z) are reduced by corrosion allowance and mill tolerance.
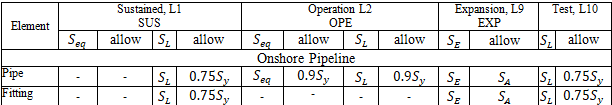
Sustained, Operating, Expansion, and Test stresses:
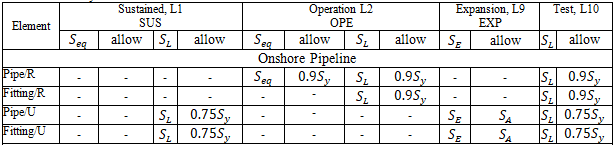
START Smart Check:
Stresses from occasional loads:
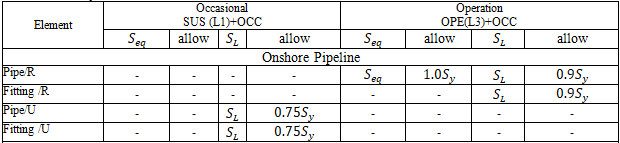
START Smart Check for occasional loads:
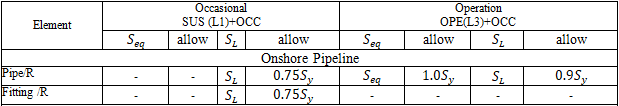
Stress calculations depend on:
"Add axial force and torsion stress" in Project Settings
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
Restrained/Unrestrained designation: Manual, Autodetect, or START Smart Check in Project Settings
Pipeline location: Onshore Pipeline (BS PD 8010-1) or Offshore Pipeline (BS PD 8010-2) in Pipe Properties
Pipeline type: Riser/landfall or Seabed including tie-in in Pipe Properties
Corrosion allowance and mill tolerance do not affect stresses except for risers.
Sustained, Operating, Expansion, and Test stresses:
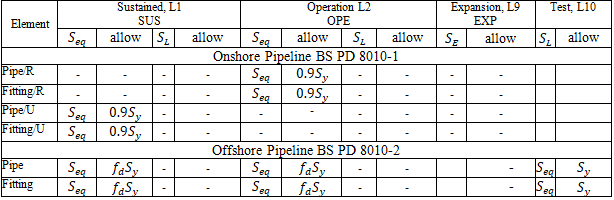
START Smart Check:
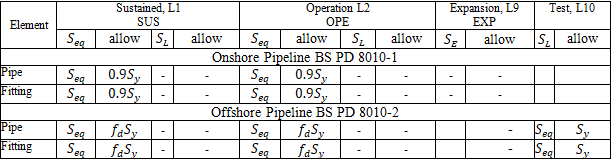
Button |
Property |
Description |
Hoop Stress |
Onshore:
Offshore:
|
|
|
Stress due to sustained or occasional loads, SL |
Onshore Pipeline (BS PD 8010-1): Restrained: Not checked Unrestrained:
START Smart Check:
Offshore (BS PD 8010-2):
A - cross-sectional area, Mi - in-plane moment, Mo - out-of-plane moment, Mt - torsional moment, Z - section modulus |
Allowable stress from sustained or occasional loads |
Onshore Pipeline:
Offshore
Sy - Yield Stress from material database |
|
|
Stress due to operation loads, SL |
Onshore Pipeline: Restrained:
F - axial force without Bourdon effect Unrestrained: Same as sustained START Smart Check: Same as sustained Offshore: Same as for sustained loads |
Allowable stress from sustained or occasional loads |
Onshore Pipeline:
Offshore
Sy - Yield Stress from material database |
|
|
Stress due to sustained in test state, SL |
Same as sustained |
Allowable stress from sustained loads in test state |
Same as sustained, but
|
Stress calculations depend on:
"Add axial force and torsion stress" in Project Settings
"Stress range from operation to cold" in Project Settings
Restrained/Unrestrained designation: Manual, Autodetect, or START Smart Check in Project Settings
Corrosion allowance and mill tolerance do not affect stresses except for risers
Sustained, Operating, Expansion stresses:
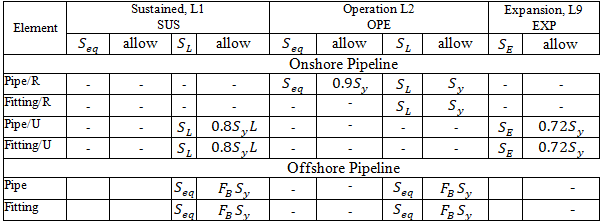
START Smart Check:
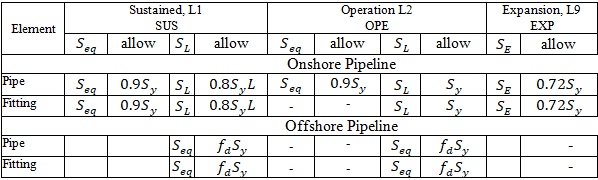
Button |
Property |
Description |
Hoop Stress |
|
|
|
Stress due to sustained or occasional loads, SL Allowable stress |
Onshore Pipeline: Restrained: Not checked Unrestrained:
START Smart Check:
Offshore (Ch.11):
A - cross-sectional area, Mi - in-plane moment, Mo - out-of-plane moment, Mt - torsional moment, Z - section modulus |
|
Stress due to operation loads, SL |
Onshore Pipeline: Restrained:
F - axial force without Bourdon effect Unrestrained:
START Smart Check:
Offshore: Same as for sustained loads |
Expansion Stress |
|
|
Stress from thermal expansions, weight, and seismic wave propagation effect |
Two checks are performed. First check:
Second check:
F - Axial force from thermal expansions, pressure Bourdon effect, weight, and seismic wave propagation effect E - Elastic modulus t - Pipe wall thickness D - Pipe outside diameter |
Bend stress intensification and flexibility factors calculated using equations:
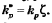
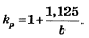
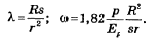
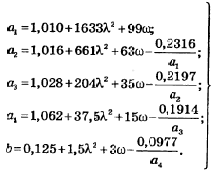
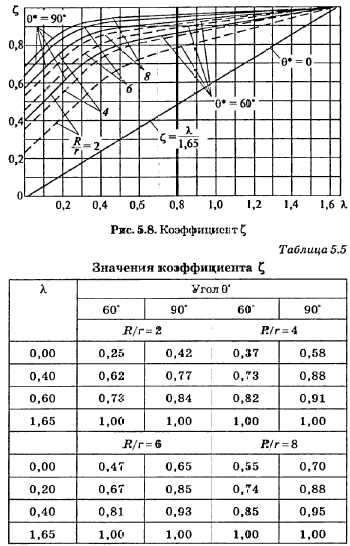
[σ]op - allowable stress at operation temperature Top, [σ]20 - allowable stress at normal temperature
[σ]op - allowable stress at operation temperature Top, [σ]20 - allowable stress at normal temperature
Please refer to Thermoplastic Piping Stress Analysis
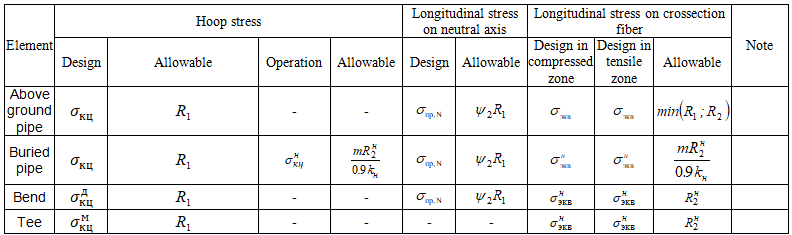
Stress table for SNIP 2.05.06-85 looks like this:
No. |
Note |
Code |
Description |
N218 |
Temperature range exceeds limit |
Strength
condition not met: |
|
N219 |
Insufficient wall thickness |
Strength
condition not met: |
|
N221 |
Structure does not meet strength conditions |
One
of strength conditions not met: |
|
N265 |
Failed stress check from pressure and weight loads |
All other codes |
Strength condition not met: S > Sallowable |
N268 |
Failed stress check in operating condition |
All other codes |
Strength condition not met: S > Sallowable |
N269 |
Failed stress check in cold condition |
All other codes |
Strength condition not met: S > Sallowable |
N284 |
Failed fatigue strength check |
All other codes |
Fatigue failure condition not met: S > Sallowable |
N676 |
Failed wall buckling check in test condition |
All other codes |
Strength condition not met: S > Sallowable |
N677 |
Failed wall buckling check in operating condition |
All other codes |
Strength condition not met: S > Sallowable |
N678 |
Failed wall buckling check in cold condition |
All other codes |
Strength condition not met: S > Sallowable |
After analysis: Output > Piping Stress