This function applies to non-reinforced rigid thermoplastic piping systems.
For reinforced thermoplastic piping, use the fiberglass piping code.
For flexible plastic piping, use the flexible plastic piping function in START-Elements.
Key differences between thermoplastic and steel piping analysis:
Allowable stress depends
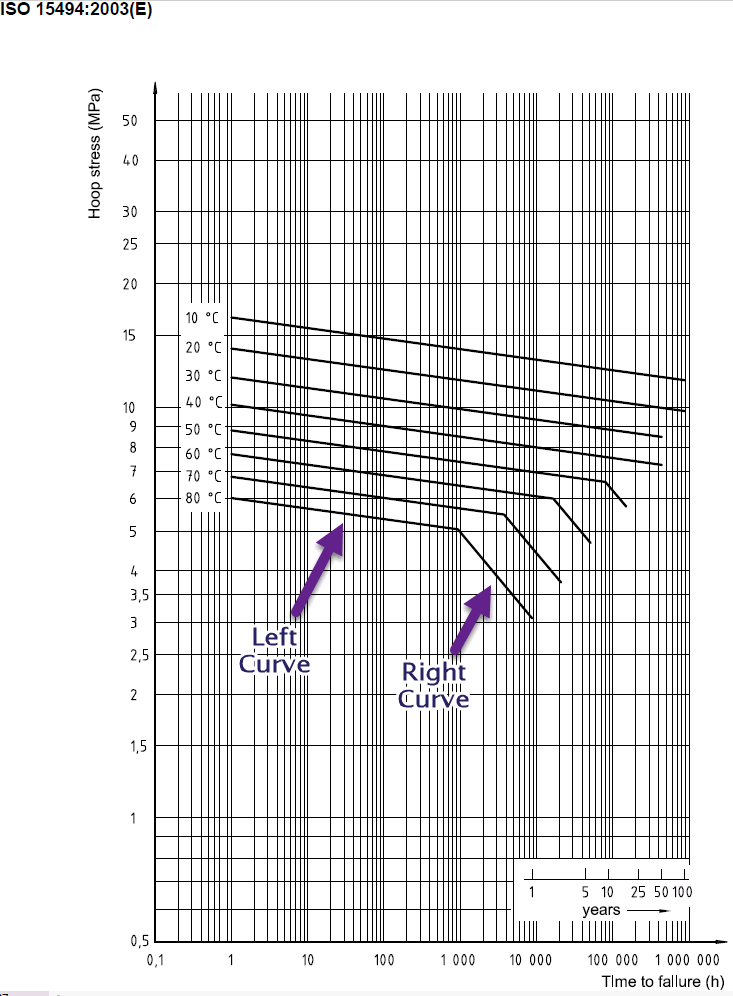
on service life and temperature, calculated using the equation: 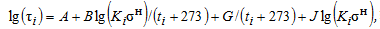 . Material-specific A, B, G, J factors are stored in
the material
database. See Stresses in
Piping for calculation details.
. Material-specific A, B, G, J factors are stored in
the material
database. See Stresses in
Piping for calculation details.
Thermal expansion coefficients are significantly higher than steel, resulting in greater thermal expansion (ε₁)
Pressure-induced expansion (ε₂) from the Bourdon effect is substantial and must be considered
Chemical swelling strain (ε₃) may require consideration. Specify swelling values in pipe additional properties
Stresses are calculated using creep modulus (Ecm) that varies with service life and stress level. Support loads use 100-minute modulus (Esm). Occasional loads use 0.1-hour modulus (Est)
Operating condition analysis uses average creep modulus between installation and operating temperatures
Poisson's ratio is temperature-dependent, approaching 0.5 at elevated temperatures

Allowable stress incorporates chemical resistance, installation condition, safety, and joint strength factors
Wall thickness checks are performed only for straight pipes, not fittings
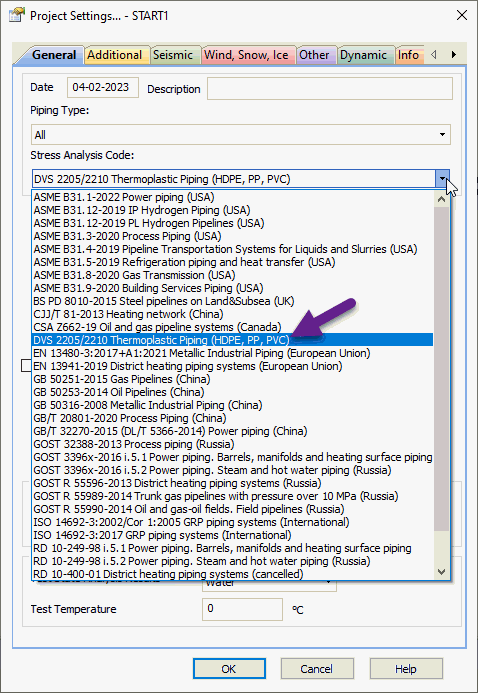
PASS/START-PROF uses the DVS 2205/2210 method for thermoplastic piping analysis.
Total axial expansion in thermoplastic pipes:
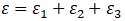
Thermal expansion (ε₁):

k - Temperature range factor from pipe additional properties, α - Thermal expansion coefficient from material database
Pressure expansion (ε₂):

t - Wall thickness, D - Outer diameter, μ - Poisson's ratio, p - Operating pressure, Ecm - Average creep modulus
Swelling expansion (ε₃):
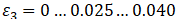
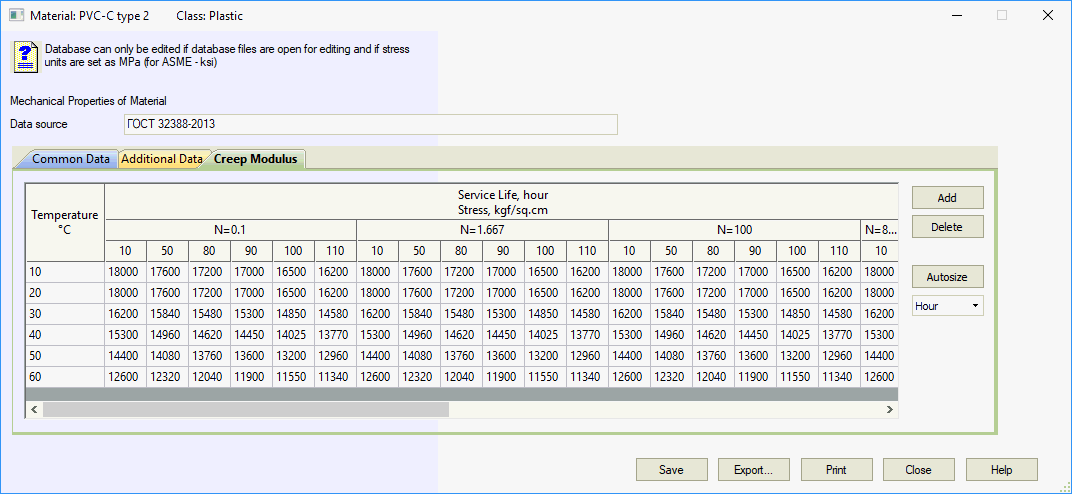
Creep modulus depends on service life (Project Settings), temperature, and stress level.
Three creep modulus types are used:
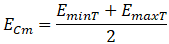
EminT - Creep modulus at ambient temperature, service life, and current stress from material database
EmaxT - Creep modulus at operating temperature, service life, and current stress from material database
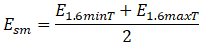
E1.6minT - Creep modulus at ambient temperature, 100-minute service life, and current stress
E1.6maxT - Creep modulus at operating temperature, 100-minute service life, and current stress

E0.1minT - Creep modulus at ambient temperature, 0.1-hour service life, and current stress
E0.1maxT - Creep modulus at operating temperature, 0.1-hour service life, and current stress
Creep modulus relationships in material database:
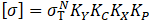
Ky - Safety factor from pipe properties
Kc - Joint strength factor from pipe properties
Kx - Chemical resistance factor from pipe properties
Kp - Installation condition factor from pipe properties
Kt = 1, Kcyc = 1
 -
Nominal long-term allowable stress
-
Nominal long-term allowable stress
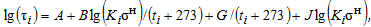
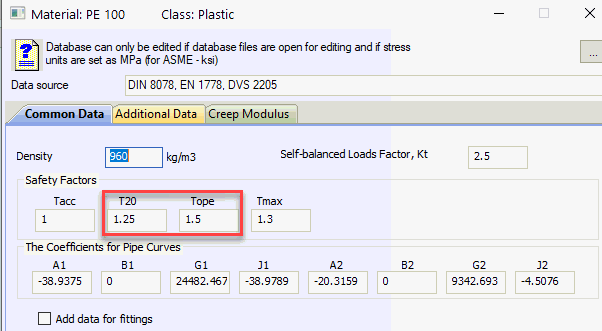
A1, B1, G1, J1 - Characteristic factors for left curve from material database
A2, B2, G2, J2 - Characteristic factors for right curve (set to zero if single curve used)
 -
Service life from project settings
-
Service life from project settings
 -
Operating temperature from pipe properties
-
Operating temperature from pipe properties
 -
Temperature safety factor from material database
(K20 for ≤20°C, Kope for >20°C)
-
Temperature safety factor from material database
(K20 for ≤20°C, Kope for >20°C)
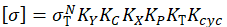
 -
Service life from project settings
-
Service life from project settings
Kt - Secondary stress factor from material database (PVC/PVC-C: 1.75, PE/PE-RT: 2.5, PVDF: 3.5, PP: 2.5)
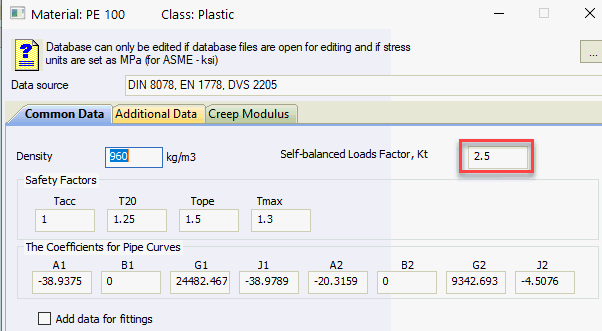
Kcyc - Fatigue factor

N - Total cycles (annual cycles × service life) from Temperature Cycles
Kcyc range: 0.4 to 1.0
Other factors follow sustained load calculation rules
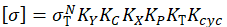
 -
Service life from project settings
-
Service life from project settings
 -
Ambient temperature from Project Settings
-
Ambient temperature from Project Settings
Other factors follow operating condition calculation rules
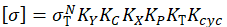
Ky = 1, Kx = 1, Kp = 1, Kt = 1, Kcyc = 1
 =
24 hours
=
24 hours
 -
Test temperature from pipe properties
-
Test temperature from pipe properties
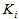 -
Occasional load safety factor (Kacc) from material
database
-
Occasional load safety factor (Kacc) from material
database
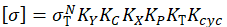
Ky = 1, Kx = 1, Kp = 1, Kt = 1, Kcyc = 1
 =
24 hours
=
24 hours
 -
Operating temperature from project settings
-
Operating temperature from project settings
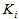 -
Occasional load safety factor (Kacc) from material
database
-
Occasional load safety factor (Kacc) from material
database
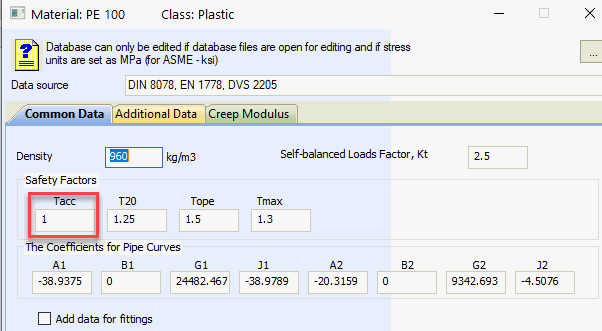
Hoop Stress

Axial Stress

Torsion Stress

Equivalent Stress

p - Pressure
D - Outer diameter
t - Wall thickness
A - Cross-sectional area
Z - Section modulus
Mt - Torsion moment
Mi - In-plane moment
Mo - Out-of-plane moment
 - Ring bending stresses from nonlinear FEM model
- Ring bending stresses from nonlinear FEM model
Bends:
Straight Tees:
Reducing Tees:

Reducers:
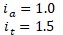
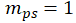
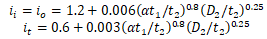
PVC-C pipe crack caused by excessive torsion from thermal expansion. START-PROF analysis during design can prevent such failures.