

Gimbal expansion joints allow elastic rotation of connected pipe ends around vertical and horizontal axes. They restrict mutual pipe rotation and all linear displacement. Typical design shown below.

Hinged expansion joints allow rotation around one axis. Typical design shown below.

Retrieve expansion joint properties from the expansion joints database by clicking the "..." button and selecting the appropriate joint.
View expansion joint analysis results in the Expansion Joint Deformation Table. See also "How to Reduce Nozzle Loads in START-PROF".
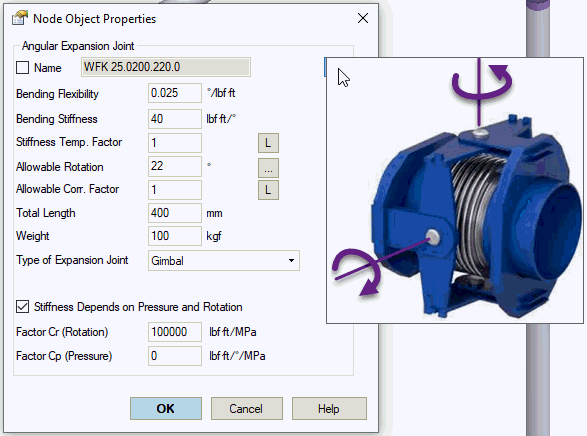

Property |
Description |
Name |
Element name. Displays in 3D view when checked. |
Bending Flexibility |
Bending flexibility (1/KR) of entire expansion joint length (all convolutions). Obtain value from manufacturer. |
Bending Stiffness |
Bending Stiffness (KR) of entire expansion joint length (all convolutions). Obtain value from manufacturer. Unlike finite length flexible elements, no need to multiply manufacturer-provided bending stiffness by 4, as expansion joints are modeled with zero length. Calculate bending angular stiffness using EJMA equation:
Kx = Axial stiffness of the bellows Dm = Effective diameter (mean bellows diameter) |
Stiffness Temp. Factor |
Elevated temperatures reduce material elastic modulus, requiring stiffness adjustment. This temperature correction factor equals the ratio of elastic modulus at operating versus ambient temperature for bellows material. Specify for each operating mode based on temperature.
|
Allowable rotation |
Maximum allowable rotational deformation. Used for expansion joint deformation analysis. Obtain value from manufacturer. |
Allowable Corr. factor |
Allowable movements reference specific load cycles and pressure. Adjust to actual cycles and pressure. Specify this correction factor for each operating mode based on pressure.
|
Length |
Expansion joint length Lu. PASS/START-PROF models this type as zero-length expansion joint internally, adding two rigid elements of length Lu/2 on both sides. Model non-zero-length expansion joints using Flexible Element. |
Weight |
Expansion joint weight applied to rigid elements (half on left, half on right). |
Type of expansion joint |
Select type: Gimbal or Hinged. |
Tie rod plane |
Select tie rod location plane: Vertical, horizontal, or custom. Example shows "Vertical":
For custom selection, specify angle between Zm local axis and tie rods plane. 0° = vertical, 90° = horizontal. |
Stiffness depends on pressure and rotation |
Account for hinge friction moment in angular expansion joints.
P – Internal pressure θ – Angular movement KRi – Angular stiffness on iteration i Ca - Bending stiffness (KR) Algorithm: 1. Set bellows angular stiffness KR0=Ca+P*Cp, perform analysis, obtain rotation angle θ 2. Set bellows angular stiffness KR1=Ca+P*Cp+(Cr*P)/θ, perform analysis, obtain new rotation angle θ 3. Repeat step 2 PASS/START-PROF automatically performs iterations. Typically 3 iterations achieve convergence. |
Factor Cr (rotation) and Cp (pressure) |
Obtain Cr and Cp factors from expansion joint manufacturer. Example: WITZENMANN provides:
|
Insert > Expansion Joint > Angular