Learn about PASS/START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
Friction factor range: μ=0.05÷0.75. Use μ=0 to exclude friction effects.
Friction coefficient μ depends on support surface materials (pipe-to-steel or shoe/cradle interface). Standard value: μ=0.3.
Carbon Steel to Carbon Steel: μ=0.2 (new) to μ=0.75 (corroded), recommended μ=0.3
Polished Stainless Steel to Polished Stainless Steel: μ=0.15
Graphite on Steel: μ=0.1
Carbon Steel on Concrete: μ=0.57-0.7
Pipe on Sand Soil: μ=0.4
Carbon Steel on PTFE: μ=0.2
Polished Stainless Steel on PTFE: μ=0.1
PTFE on PTFE: μ=0.1-0.15
Steel on Ice: μ=0.05
Pipe on Roll/Ball Support: μ=0.05
Apply friction factors to all vertical restraints. For guide and horizontal restraints, company standards vary—some exclude friction, others use values above.
Friction significantly impacts piping system behavior, especially for:
Long transmission pipelines (balances thermal expansion forces)
Rotating equipment connections (critical due to low allowable loads)
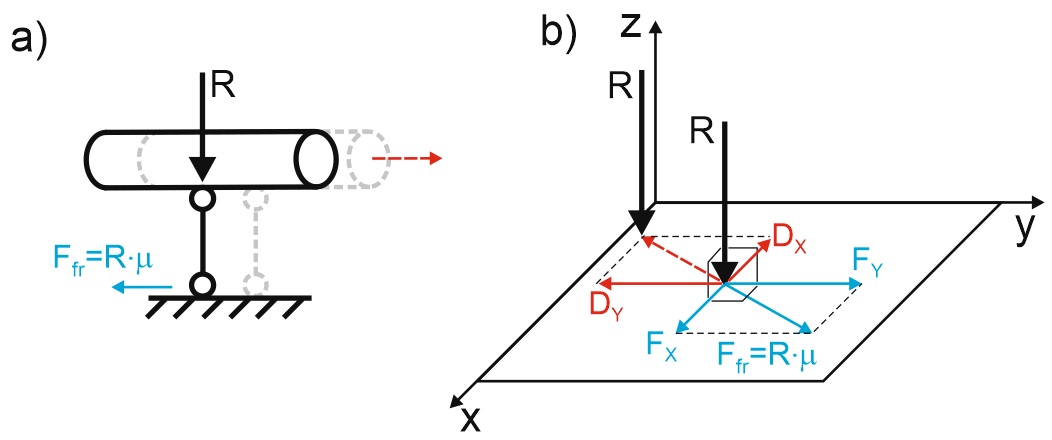
Friction restraints are nonlinear, with sliding surfaces perpendicular to restraint directions.
Friction Force: Ffr = R × μ
No Movement: When (Fx² + Fy²)0.5 < Ffr, displacements Dx=0, Dy=0
Movement Initiation: When (Fx² + Fy²)0.5 = Ffr
Force Direction: During movement, friction force vector parallels displacement vector: Fx/Dx = Fy/Dy

Friction Restraint Behavior
Friction diminishes during vibration. Use friction multipliers of 0 or 0.5 in the Operation Mode Editor for dynamic loads:
Friction forces develop during heating (installation to operating mode) and reverse during cooling (operating to cold mode). This directional change significantly affects anchor reactions, particularly in buried pipelines with high friction forces.
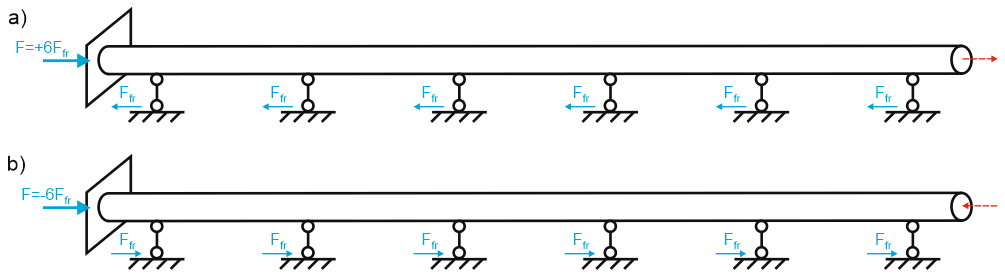
(a) Heating: Installation → Operating mode
(b) Cooling: Operating → Cold mode