

Learn more about START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
START-PROF calculates support loads and stresses from relief valve discharge using static analysis methods.
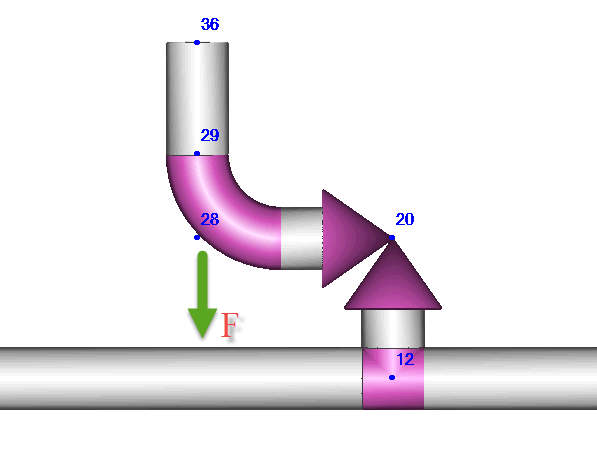
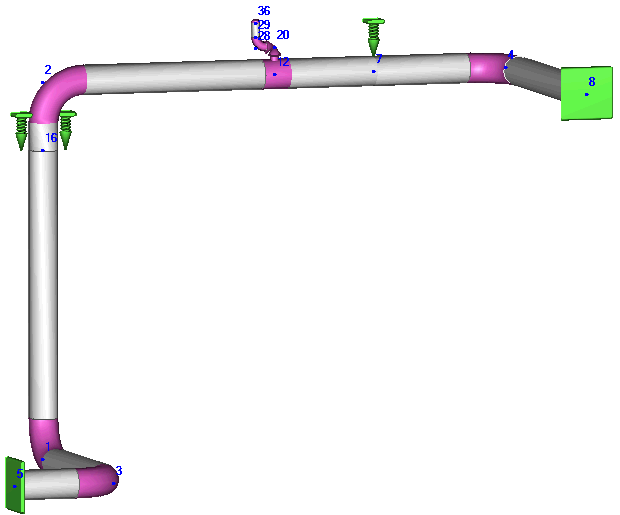
The relief valve thrust load acts on elbow 28. Apply this force at the elbow end (node 29) in START-PROF.
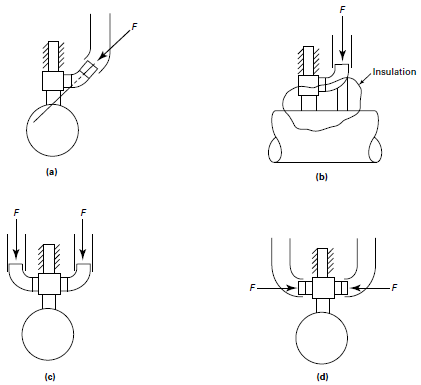
Calculate the equivalent dynamic thrust force F using these methods:
Calculate equivalent dynamic thrust force:
F = DLF ∙ F1
Where:
DLF - dynamic load factor, based on piping natural period. Use DLF=2.0 if period is unknown.

F1 - static reaction force (N):
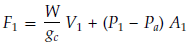
Where:
W - mass flow rate (valve relieving capacity × 1.11), kg/sec
gc = 1 - gravitational constant
Pa - atmospheric pressure, N/m²
A1 - exit flow area, m²: A1 = π(D-2t)²/4
V1 - exit velocity (node 36), m/sec
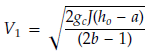
P1 - static pressure, N/m²
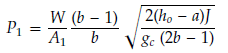
h0 - stagnation enthalpy at safety valve inlet, MJ/kg
J = 999835.0529 m*N/MJ
a, b - constants from table below
Steam Condition |
a, MJ/kg |
b |
Wet
steam |
0.6769 |
11 |
Saturated
steam |
1.9143 |
4.33 |
Superheated
steam |
1.93291 |
4.33 |
Example project file: ReliefValve.ctp
Input data:
Discharge pipe diameter: 0.219 m
Discharge pipe wall thickness: 0.016 m
Product: Saturated steam
Relief valve capacity: 48 kg/sec
Steam pressure: 64 kgf/cm²
Steam temperature: 538°C
Calculation:
A1 = π(D-2t)²/4 = 3.14159×(0.219-2×0.016)²/4 = 0.027465 m²
a = 1.9143 MJ/kg
b = 4.33
W = 48×1.11 = 53.28 kg/sec
Stagnation enthalpy for steam at 64 kgf/cm² and 538°C: h0 = 3.506 MJ/kg
J = 999835.0529 m*N/MJ
P1 = 53.28/0.027465×(4.33-1)/4.33×(2×(3.506-1.9143)×999835.0529/(2×4.33-1)/1)^0.5 = 961693 N/m²
V1 = (2×999835.0529×(3.506-1.9143)/(2×4.33-1))^0.5 = 644.6 m/sec
F1 = 53.28×644.77 + (961693-100000)×0.027465 = 58019 N
F = DLF × F1 = 2×58019 = 116039 N
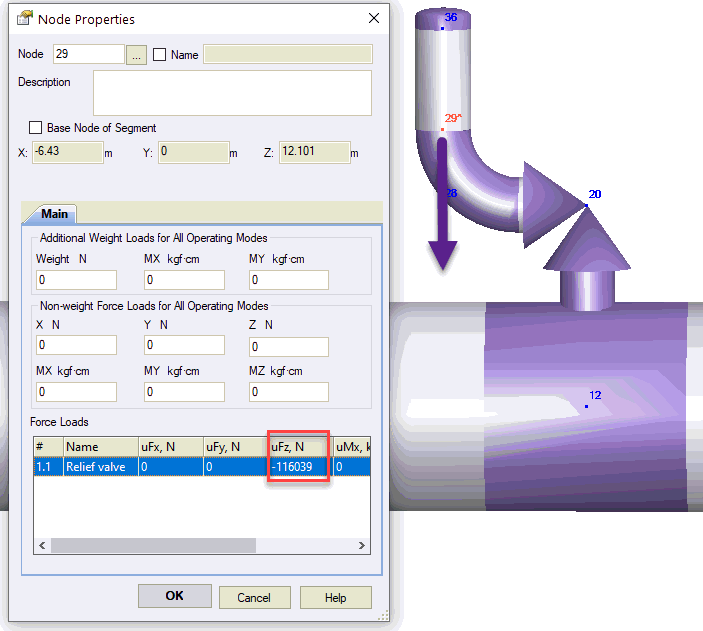
Create occasional force loading 1.1 in the operation mode editor:

For multiple relief valves, create additional modes (1.2, 1.3, etc.) if they operate independently.
Apply dynamic thrust force at node 29 for mode 1.1:
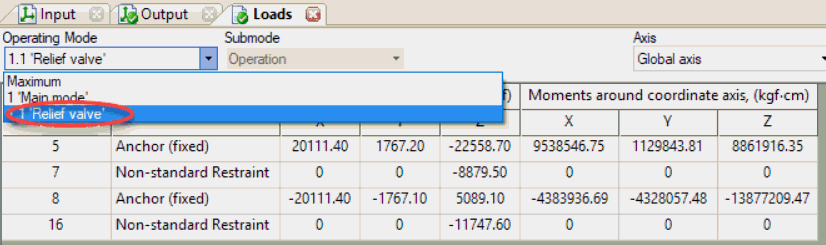
Support loads from relief valve thrust:
Stresses from relief valve thrust:
