Learn more about PASS/START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
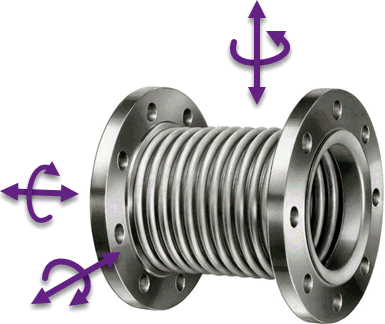
Universal expansion joints consist of simple bellows without tie rods. They accommodate bending, compression, tension, lateral, and torsional movements.

Retrieve expansion joint properties from the expansion joints database by clicking the "..." button and selecting the appropriate model.
View expansion joint analysis results in the Expansion Joint Deformation Table. See also How to Reduce Nozzle Loads in PASS/START-PROF.
Universal expansion joints are available with one or two bellows and can be configured as pressure balanced units.
Property |
Description |
Name |
Element identifier. When checked, displays in the 3D model view. |
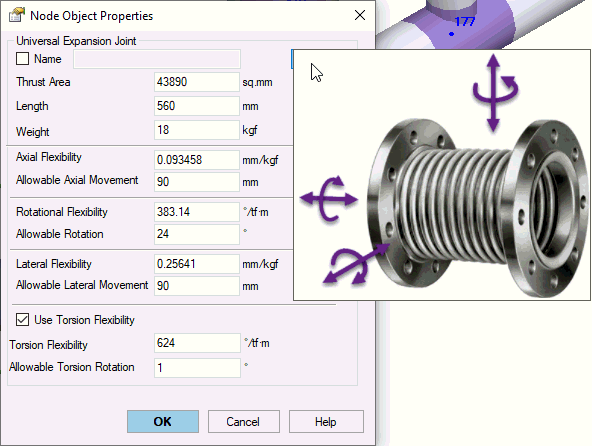
Effective area1 |
Expansion joint effective area for thrust force calculation. More information... For bellows, calculate effective area Aeff using the circle area formula with effective mean diameter Deff: Aeff = π × (Deff)² / 4 Approximate Deff as (Dmin + Dmax)/2. Obtain exact values from manufacturer specifications. Set Aeff = 0 for pressure balanced expansion joints. |
Length |
Expansion joint length Lu. PASS/START-PROF models this expansion joint type with zero length internally, adding two rigid elements of length Lu/2 on each side. Model non-zero length expansion joints using Flexible Elements. |
Weight |
Expansion joint weight distributed equally to adjacent rigid elements (half to left, half to right). |
Axial Flexibility1 |
Axial flexibility (1/Kax) for full expansion joint length (all convolutions). Kax represents axial stiffness. Obtain values from manufacturer data. |
Axial Allowable Deformation, Δk1 |
Maximum allowable axial movement (Δk/2), where Δk represents full allowable axial travel. Used for expansion joint deformation analysis. Obtain values from manufacturer specifications. |
Rotational Flexibility1 |
Rotational flexibility (1/Kb) for full expansion joint length. Kb represents bending angular stiffness. Obtain values from manufacturer data. No 4x multiplier required since expansion joint is modeled as zero length. Calculate bending angular stiffness using EJMA equation: Kb = Kax × Deff² / 8 Where: Kax = Bellows axial stiffness Deff = Bellows effective diameter |
Allowable Rotation1 |
Maximum allowable rotation angle. Used for expansion joint deformation analysis. Obtain values from manufacturer specifications. |
Lateral Flexibility1 |
Transverse lateral flexibility (1/Ktr) for full expansion joint length. Ktr represents transverse lateral stiffness. Obtain values from manufacturer data. Calculate transverse lateral stiffness using EJMA equation: Ktr = 1.5 × Kax × (Deff/L)² Where: Kax = Bellows axial stiffness Deff = Bellows effective diameter L = Total bellows length (all convolutions) |
Allowable Lateral Deformation1 |
Maximum allowable lateral movement. Used for expansion joint deformation analysis. |
Note 1: Retrieve thrust area, flexibility, and allowable axial movement from the expansion joints database by clicking the "..." button and selecting the appropriate expansion joint.
After analysis, PASS/START-PROF checks flexible joint relative displacements using the following equation:

When allowable torsion rotation is specified, the equation includes a fourth term.