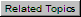
1 - backfill soil, 2 - expansion cushion, 3 - foundation soil

Pipe-soil interaction methods use experimental and theoretical data. This implementation is a modified and improved version of [1]. Key methodology details are covered in the pipe-soil interaction model.
Define main and additional properties for buried elements as you would for standard above-ground elements. To account for soil effects, select "Buried element" to access the additional soil properties tab.
Burial depth, water table height, and soil subsidence can vary along the pipe length. Input these values at both element start and end points. Since these parameters are nodal properties, values must match at shared nodes. Changing a value at one node automatically updates it for all connected elements.


Property |
Description |
Submerged Pipe |
Enable/disable water buoyancy effects and changes to soil properties when saturated |
Water height, Hws, Hwe |
Vertical
distance from pipe centerline to water table. Accepts positive
or negative values. Affects buoyancy forces (pipe flotation)
and soil resistance to longitudinal/vertical movement (due
to property changes in saturated soil). More... |
Consider Soil Movements |
Enable/disable soil movement effects. Use to model soil subsidence, frost heave, landslides, seismic displacements, or permanent ground deformation |
Soil Movement x,y,z |
Models soil subsidence (-Z), frost heave (+Z), landslides (any X,Y,Z direction), permanent ground deformation, or seismic fault crossings. Define soil spring displacements in the global coordinate system. Values can vary along the element length - input at start and end nodes. If adjacent elements have soil movement disabled, the program gradually transitions from specified values to zero at the connection point.
|
Backfill soil height, Hs, He |
Distance from ground surface to top of insulation casing. H = Z - (DC / 2). When H is specified, Z calculates automatically, and vice versa. Not applicable for elements angled more than 10 degrees from horizontal. |
Laying depth, Zs, Ze |
Distance
from ground surface to pipe centerline. When H is specified,
Z calculates automatically, and vice versa. |
Backfill soil number1 |
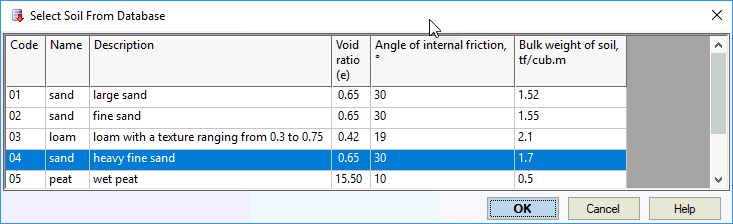
Trench backfill material. Select from the soil database (see note 1 below). |
Base soil number1 |
Native (undisturbed) foundation soil. Select from the soil database (see note 1 below). |
Pipe laying type |
Open trench method: soil arching is ignored. Soil pressure calculations use full trench depth. Trenchless method (e.g., directional drilling): accounts for soil arching. Soil pressure calculations use reduced depth based on natural arch height. Read more...
|
Insulation type2 |
Armopenobeton, polymer, polyurethane, other, or no insulation. For polyurethane, casing diameter DC and thickness SC auto-populate from the database based on pipe diameter D. For other insulation types, enter these values manually. |
Insulation casing diameter1, DC |
External
insulation casing OD. Auto-populates via Enter 0 to use pipe outer diameter as default. |
Casing wall thickness1, SC |
External
insulation casing wall thickness. Auto-populates via |
Factor NM |
In Aynbinder's model: accounts for friction angle differences between insulation-soil and metal-soil interfaces. Depends on external insulation material load characteristics.
Determine factor per:
Recommended: NM=0.67 for PE casing insulation, NM=1.0 for bare pipe. In ASCE 2001 model: NM equals factor f - coating factor relating soil internal friction angle to soil-pipe interface friction angle.
In EN 13941 model:
|
Expansion cushions |
Enable/disable damping cushion effects. Note: cushions don't always increase allowable axial movement and may reduce functionality in some cases. Not available for elements angled more than 10 degrees from horizontal. |
Note 1: Click the soil selection button to open a dialog with all soil types from the soil database:
To create a new buried element:
Method 1:
Create an above-ground element
Select it and click  on the toolbar
on the toolbar
Verify element properties (double-click or use
 toolbar
icon)
toolbar
icon)
Method 2:
Create an above-ground element
Open the element editor and press CTRL+Enter to access the soil properties tab
To view existing element properties:
Double-click the element in the 3D view
Select the element and click  toolbar icon
toolbar icon
1. A. Ainbinder, A. Kamershteyn Transmission pipelines stress and stability analysis. Moscow, 1982
2. GOST 30732-2006. Steel pipes and fittings with polyurethane foam insulation in polyethylene casing. Technical conditions. Russian State Committee for Construction. Moscow 2006