


Reducers can only be placed at nodes along straight pipe segments where adjoining pipes have different diameters. The reducer node is positioned at the smaller diameter end.
The reducer weight is modeled as a uniform load. The software subtracts the weight of the pipe section covered by the reducer. Insulation and fluid weights are calculated as average values from the two connected pipes. Snow, ice, wind, and user-defined uniform loads also use average values from adjacent pipes.
ASME Code Considerations:
START-PROF does not perform wall thickness checks for reducers under ASME codes. For Russian codes, the software checks wall thickness for all reducer types.

Property |
Description |
Name |
Element identifier. When checked, displays in 3D view |
Material |
Material selection from materials database |
Calculate weight automatically |
Automatically calculates reducer weight as frustum volume with linear wall thickness variation |
Weight |
Reducer weight excluding insulation and content. Enter standard weight without overload factors. Content and insulation weights with overload factors are automatically calculated from adjacent pipes |
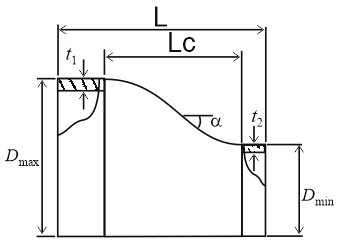
Wall thickness at Dmax, t1 |
Nominal wall thickness at maximum diameter section |
Wall thickness at Dmin, t2 |
Nominal wall thickness at minimum diameter section |
Mill tolerance |
Manufacturing tolerance for wall thickness. More... |
Corrosion and wear allowance |
Additional wall thickness allowance for corrosion and wear. More... |
Cone length, Lc |
Length of conical reducer section |
Full length, L |
Total reducer element length |
Cone Angle, α |
Slope angle of conical section. k=1 for eccentric reducers
|
Longitudinal Weld Joint Efficiency Factor, E |
Longitudinal weld joint efficiency factor. More... |
Manufacturing technology |
For ASME B31.3, DL/T 5366-2014: seamless pipe uses Wl=1.0, electric-welded pipe uses database values. More... For GOST 32388-2013, material properties vary by pipe type (seamless/welded) from materials database. |
Angle between shear direction and local axis Zm |
Angle between shear direction and adjoining element local axis Zm. Defines eccentricity orientation in space. Use 0° for vertical eccentricity. |
Stress correlation along two axes, r |
Based on ISO 14692 section 7.10
|
Qualified stress, qs |
If blank, uses value from material database Based on ISO 14692 section 7.8
|
Internal protective layer thickness |
|
External protective layer thickness |
|
To insert a reducer: select the target node and use Insert > Insert Reducer > Insert Eccentric Reducer
To view existing element properties:
Double-click the element in 3D view
Select the element and click  toolbar icon
toolbar icon