
Learn more about PASS/START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
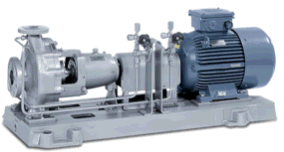
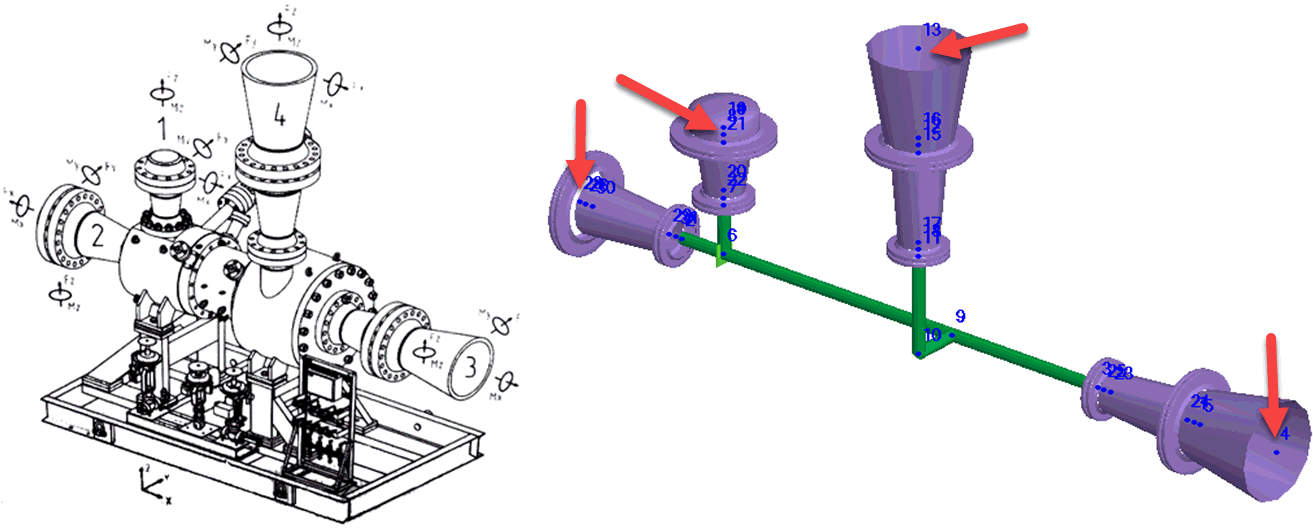
Model centrifugal pumps and verify nozzle loads per ISO 5199 requirements. Each pump object connects to one or two nodes. The software checks allowable loads for individual nozzles and the complete pump assembly.
View analysis results in the Nozzle and Equipment Loads Table. See also Nozzle Load Reduction Methods in PASS/START-PROF
Pump Modeling Approaches:
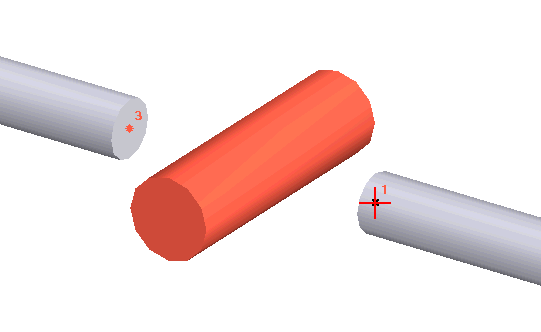
1. Nozzles at Pipe Terminations
Connect pump nozzles to pipe end nodes. The system automatically models pump nozzles as fixed anchors and simulates thermal expansion as anchor displacement.
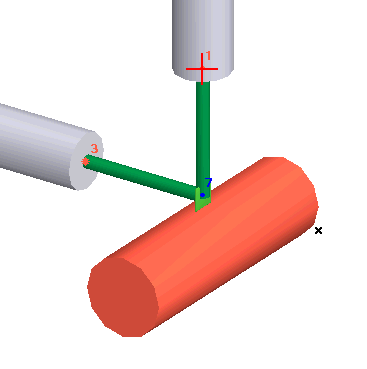
2. Nozzles at Intermediate Locations
Connect pump nozzles to intermediate nodes. Manually construct the pump model using rigid elements, cylindrical shells, and other components. Model thermal expansion through element temperature properties.
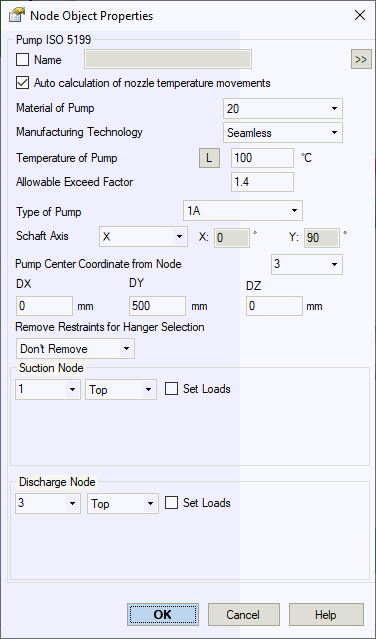
Property |
Description |
Name |
Element identifier. When enabled, displays in 3D view |
Auto-calculate nozzle thermal movements |
Automatically computes nozzle displacements as DX*α*(T-Ta), DY*α*(T-Ta), DZ*α*(T-Ta), where α is the thermal expansion coefficient (from material properties), T is equipment temperature, Ta is ambient temperature, and DX, DY, DZ are distances from pump center. Disable to specify manual displacements |
Material |
Material selection from materials database |
Manufacturing technology |
For ASME B31.1, ASME B31.3, DL/T 5366-2014, seamless pipe uses Wl=1.0. Electric-welded pipe Wl values come from database. Details... For GOST 32388-2013, material properties are sourced from different databases based on pipe type (seamless/welded). |
Temperature |
Pump operating temperature. More information This
property varies by operating
mode. Click |
Allowable Exceed Factor |
Default: 1.4. Adjust per pump manufacturer specifications.
|
Pump type |
|
Shaft direction |
Shaft orientation relative to X-axis per equipment drawings:
|
Pump center point offsets |
Reference node and XYZ offsets from node to pump center (point 3 in diagrams above) |
Release restraints for spring hanger selection |
When enabled, selected restraints are temporarily removed during variable/constant spring selection weight analysis. Restraints remain active during main analysis. This technique isolates weight loading from nozzle elements, allowing springs to support loads at zero displacement positions. Options:
|
Suction nozzle Discharge nozzle |
Assign node connections for suction and discharge nozzles. Specify nozzle orientation (Top, Side, End). For unmodeled piping, select "Set Custom Loads" to manually input loads |
Set loads |
When modeling only one pump nozzle, apply manual loads to the second nozzle for ISO 5199 B.4.4 compliance checks. Enable this option to specify loads directly |
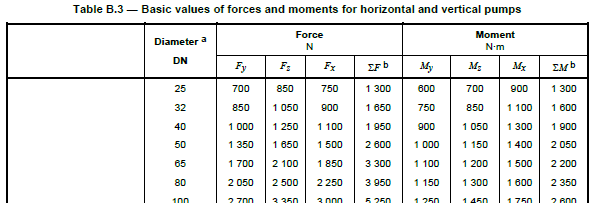
PASS/START-PROF checks nozzle loads against Table B.3 allowable values
The software performs additional verification per ISO 5199 section B.4.4 requirements
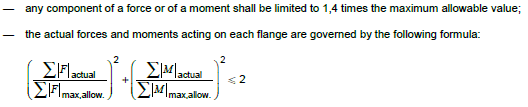
To insert a pump: Select target node and navigate to Insert > Equipment > Pump ISO 5199