

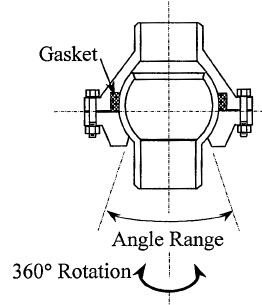
This expansion joint permits rotation of connected pipes around three axes.
Rotation occurs when resultant moment M exceeds friction moment Mf:
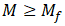
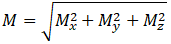
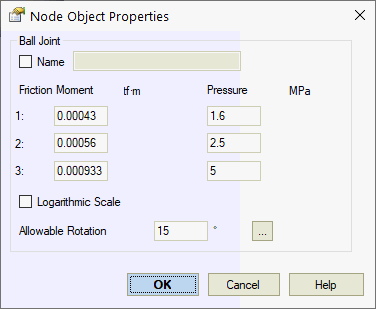
Friction moment Mf is automatically calculated using linear or logarithmic interpolation between [Mf1, P1], [Mf2, P2], and [Mf3, P3] values based on pressure P in each operating mode.
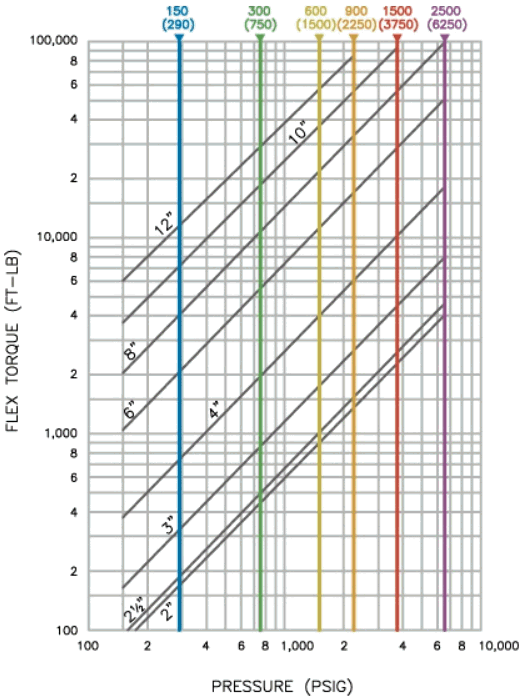
Example: ASME type HYSPAN Barco ball joints use logarithmic interpolation between [P1, M1], [P2, M2]:
Joint remains stationary when resultant moment M is less than friction moment Mf:
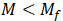
Access joint properties from the expansion joints database by clicking "..." and selecting the appropriate joint.
Analysis results appear in the Expansion Joint Deformation Table.

Property |
Description |
Name |
Element identifier. When checked, displays in 3D view. |
Friction Moment Mf1, Mf2, Mf3 |
Joint rotates when torsion moment exceeds friction moment Mf |
Pressure P1, P2, P3 |
Pressure values corresponding to friction moments Mf1, Mf2, Mf3 |
Logarithmic scale |
When enabled, uses logarithmic interpolation between [Mf1, P1], [Mf2, P2], and [Mf3, P3] values for Mf calculation per operating mode |
Allowable rotation |
Maximum allowable rotational deformation around Ym and Zm axes. Used for expansion joint deformation analysis. Obtain values from manufacturer. Allowable torsion rotation is always 360°. |
To insert a ball joint: Select target node, then choose Insert > Expansion Joint > Ball
To view ball joint properties:
Double-click in 3D view
Select and click  toolbar icon
toolbar icon