

 |
PASS/NOZZLE-FEM 3.5. Program Manual |  |
The structure attachment model is specified by a junction type with a base element, by the dimensions and section parameters, by its placement way relative to the base element, etc.
The description of the base element is given in the section: Base element setting.
Table 3.19 shows key features of the base element (shell).
| Table 3.19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Feature | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure local coordinate system (LCS), located on cylindrical or conical shells, including tank and vertical vessel: |
X-axis is directed along the local (longitudinal) Z-axis of the base element. Y-axis is directed along the normal to the ZX-plane; it is calculated as $e_y = e_z \times e_x$. Z-axis is directed along the longitudinal structure axis. The cross-section rotation angle $\omega_t$ allowes to rotate the local X and Y axes around the local Z-axis, 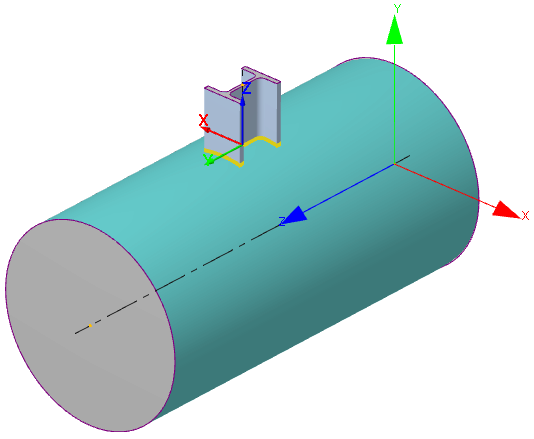 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
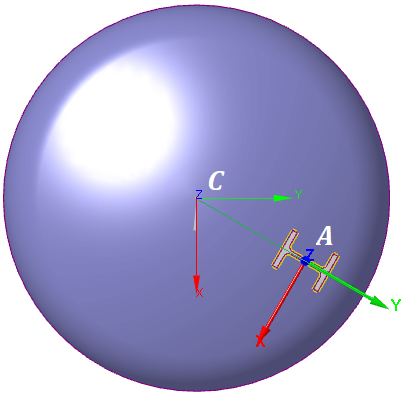
| Structure local coordinate system (LCS), located on heads: |
X-axis is directed along a straight line in the head plane passing through the center of the head and the structure end, that is from C-point to A-point (fig. 3.56). Y-axis is directed along the normal to the ZX-plane; it is calculated as $e_y = e_z \times e_x$. Z-axis is directed along the longitudinal structure axis. If the attachment is central (offset is not set), then X-axis coincides with the local X-axis of the head. The cross-section rotation angle $\omega_t$ allowes to rotate the local X and Y axes around the local Z-axis, 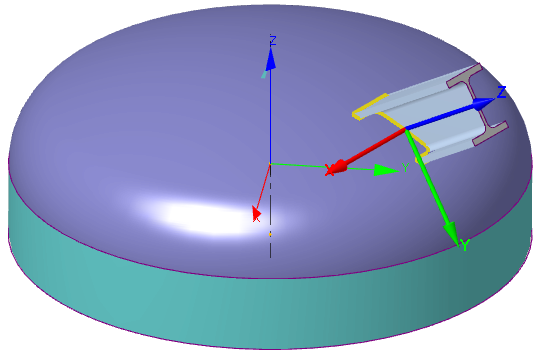
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure local coordinate system (LCS), located on elbow (bend): |
X-axis is directed along the tangential axis of the central axial curve of the elbow (bend) element. Y-axis is directed along the normal to the ZX-plane; it is calculated as $e_y = e_z \times e_x$. Z-axis is directed along the longitudinal structure axis. The cross-section rotation angle $\omega_t$ allowes to rotate the local X and Y axes around the local Z-axis, 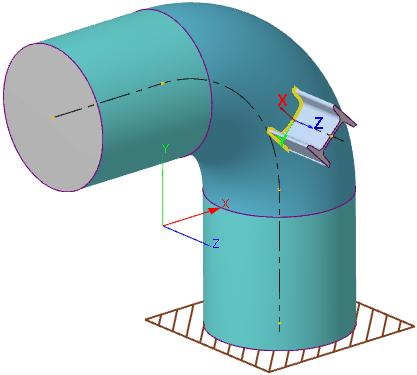 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure local coordinate system (LCS), located on rectangular plate: |
It coincides with local CS of base element (plate). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Placement in LCS of base element: | For cylindrical or conical shells, including tank and vertical vessel, the structure placement can be specified by the following types:
For elbows (bends), the structure placement can be specified by the same types as for the cylindrical shell.
For heads or rectangular plates, the placement of the structure attachment can be specified by the following types:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Constraints (dof): | Absent in the all calculation schemes. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure loads: | Thermal strains. Concentrated loads in the juncture or on the structure end. More information in the section: Setting model loads. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shell loads: | Described in the section: Base element setting. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special calculations: | Allowable loads; Stiffness and flexibility factors; Stress intensification factors; Calculation as per WRC 537(107)/297 (only for circular and rectangular sections). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure junction types: |
The structure design model corresponds to fig. 3.58.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||

PASS/NOZZLE-FEM 3.5. Program Manual
Copyright © 2017-2026, PASS Team