 button
of the Main toolbar or
using the menu item "Tools - Insulation Database..."). Please
note that when you launch the materials database editor, a dialog box
with the following message may appear:
button
of the Main toolbar or
using the menu item "Tools - Insulation Database..."). Please
note that when you launch the materials database editor, a dialog box
with the following message may appear:Editing the insulation materials database
The parameters of thermal insulation materials used in the thermal calculation of the pipeline in the program are stored in a special database of insulation materials. The materials database is an "InsulationDatabase.mdb" file, located by default in the C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\truboprovod directory. However, if necessary, the location of the database can be changed in the program settings, for more details see here. Also in this directory there may be files "Copy_InsulationDatabase.mdb" (which is a backup copy of the database), "InsulationDatabase_old.mdb" and "InsulationDatabase_old_old.mdb" (databases from previous versions of Hydrosystem) - these files are not needed to work in Hydrosystem.
If you want to view the characteristics
of existing insulation materials (their thermal conductivity coefficients,
available sizes, etc.) or edit them, or if you want to add your own material
to the database that is not in it (to then use it in calculations), all
these actions can be done using a special materials database editor, which
can be launched by clicking the  button
of the Main toolbar or
using the menu item "Tools - Insulation Database..."). Please
note that when you launch the materials database editor, a dialog box
with the following message may appear:
button
of the Main toolbar or
using the menu item "Tools - Insulation Database..."). Please
note that when you launch the materials database editor, a dialog box
with the following message may appear:
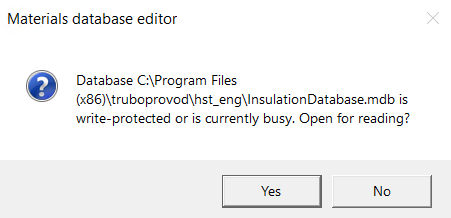
This message may appear in the following cases:
if the security policies on your computer are set up in such a way that the directory where the database file is located is read-only for your Windows account (the path to this directory is displayed in this message). In this case, it is recommended to contact the system administrator to obtain editing rights to this directory, or, if possible, run Hydrosystem as administrator, or copy the database file to another folder and set in the Hydrosystem settings a new location of this file (for more information, see here);
if the database is currently open for editing, for example, on some other computer (if you use one common materials database for several computers with Hydrosystem) or if the materials database editor is already running on your computer (for example, if you launched the database editor earlier and forgot to close it). In this case, you must close all running copies of the database editor on this and other computers using this database;
if the previous session of working with the database editor (on this or another computer using the same database file) was interrupted abnormally (for example, due to a system failure). The fact is that when opening a database for editing, a special "lock" is installed in the database file, prohibiting its simultaneous editing by another user or program. When closing the editor, this "lock" is removed, but if the work of the database editor was not completed correctly due to a failure, this "lock" may remain in the database. In this case, it is recommended to open the database for reading by clicking the "Yes" button in the above window, and then close the database editor. The "lock" will be removed, and the next time the database will be opened for editing. If the above operations did not help, contact the program's technical support.
If you only need to view the information in the database and do not need to edit anything, you can simply click the "Yes" button in this window - the database will open, but will be read-only.
Once opened, the database editor window will appear:
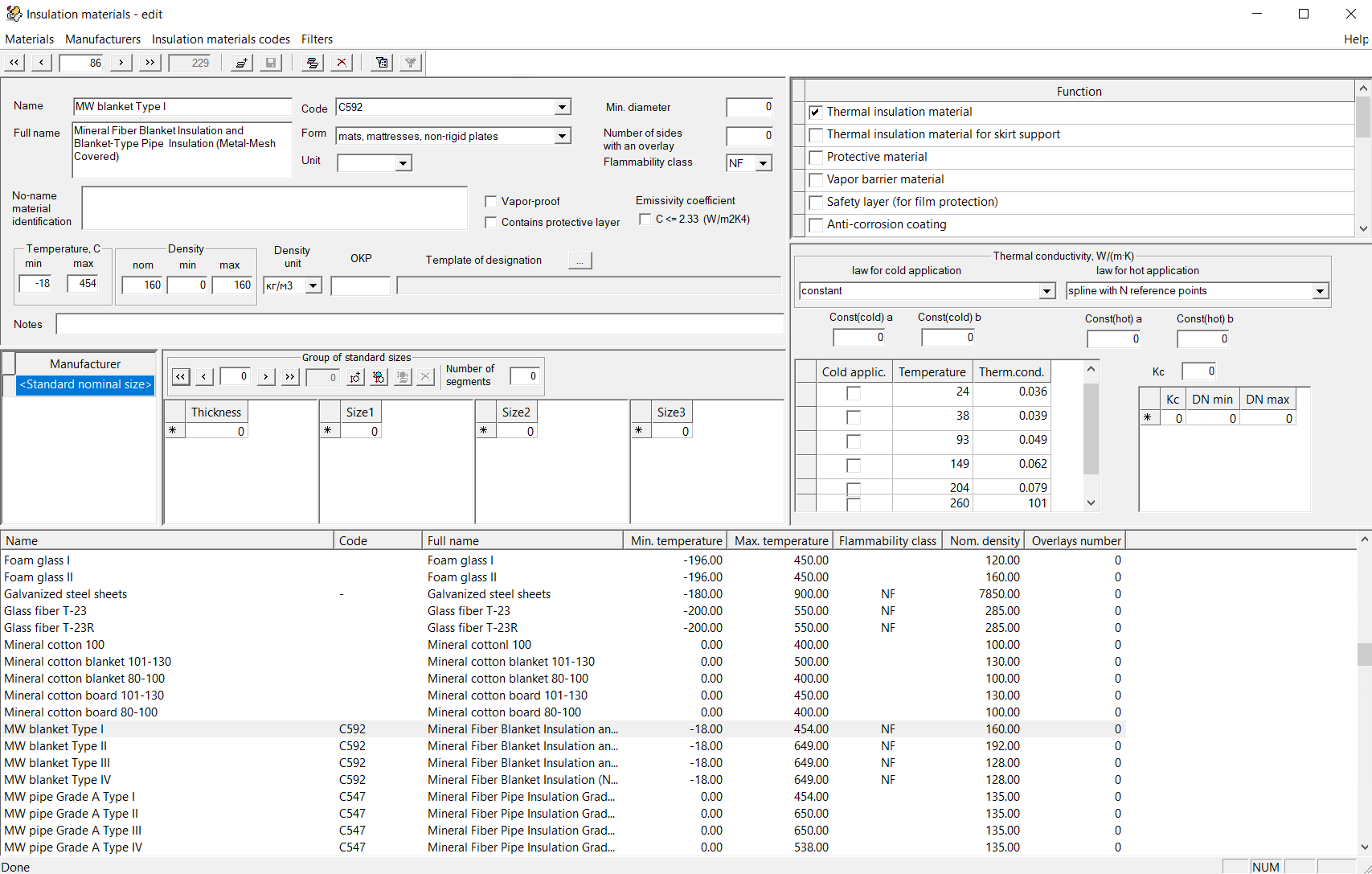
In this window, at the bottom, there is a list of all materials available in the database (thermal insulation and auxiliary). When selecting a particular material in this list, the upper windows will display its characteristics. A small toolbar and menu at the top of the window are provided for managing the database.
For more convenient navigation through the list of materials, you can "search" for a material by its first letters: to do this, select any material in the list and start typing the material name on the keyboard. As you type, the list will scroll to the first material that matches the name. In addition, to search for a specific material (or materials with specific characteristics), it is convenient to use filters by clicking on the corresponding button on the toolbar or the "Filters" menu:
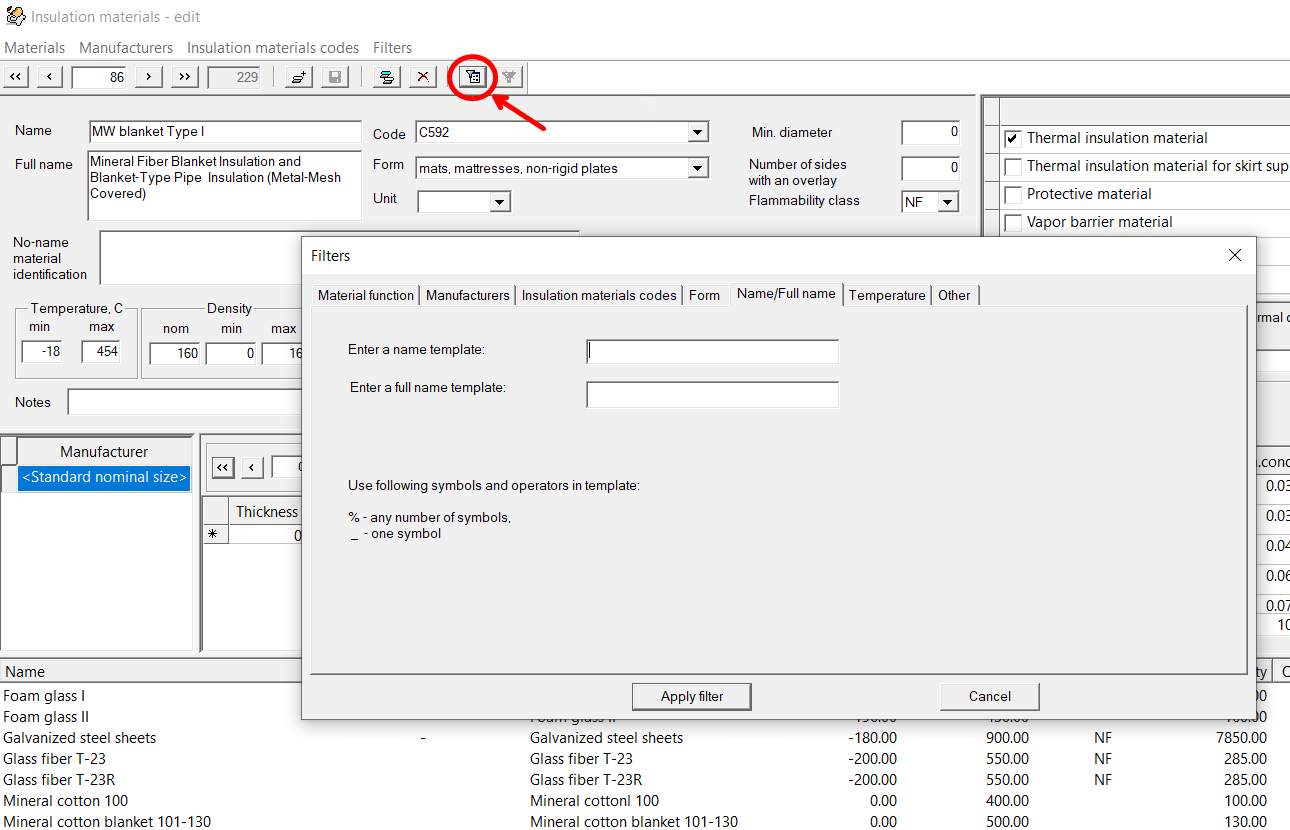
In this way, you can "filter" the database so that it displays only materials for certain purposes, and/or from a certain manufacturer, and/or having a certain shape (mats, cylinders, etc.), or by some other characteristics. In addition, filters are convenient to use if, for example, you need to find materials that can be used at certain high (or, conversely, low) temperatures. To do this, on the "Temperature" tab in the filter window, specify the maximum (or minimum) temperature that the material must withstand. You can also use filters to find a material or materials by their full/short name or its fragments. To do this, on the "Name/Full name" tab in the filter window, specify a search template by name/full name of the material. In the template, you can use the "%" sign, which replaces any number of characters, and the "_" sign, which replaces one character. For example, if you enter the Fiber-glass% in the short name template line, the database will display only materials whose short names begin with "Fiber-glass...". Or if you enter %aerogel% in the full name template line, then only aerogel based materials will be displayed (i.e., those that contain "aerogel" in the full name), etc.
You can set one filter or several filters simultaneously (in the second case, materials that satisfy all specified filters will be selected). To filter the database, click the "Apply filter" button in the filters window; to return to the original view of the database (in which all materials are displayed), click the "Clear Filter" button on the toolbar or the corresponding command in the "Filters" menu.
Editing a database usually involves either editing the characteristics of existing materials in the database or adding your own materials. In the first case, however, it is still recommended to create copies of existing materials and edit their properties so that the database also stores the original versions of all materials (in case you need them in the future). To create a copy of a material, select the material of interest in the list and use the menu item "Materials - Copy": this will copy the current material under the name "Copy of <Name of original material>". To add a new material, use the menu item "Materials - New material": this will add the material with an empty name and unfilled characteristics.
When adding/editing materials, it is important:
maintain the uniqueness of the material short name and do not add materials with short names that are already used in the database. It is important to note here that this operation is generally allowed by the database editor. This is rare, but may be necessary if, for example, the same material has different characteristics according to its various codes and it is necessary to be able to calculate the material both according to the every code (in this case, you can create a copy of the material with the same name in the database). However, in order to avoid confusion and to avoid problems in the future when merging databases (when, when updating the program, it will be necessary to import user records into a newer version of the materials database), it is recommended to use unique designations for all materials;
specify all the characteristics of the material necessary for the heat-hydraulic calculation, which include:
material short name
material function (thermal insulation material, protective material etc.)
form of thermal insulation material
data on the thermal conductivity of the material - its dependence on temperature (linear, parabolic, spline, etc.) or a constant value (constant). Please note that the dependence of thermal conductivity on temperature (or its constant value) is specified separately for "cold" use of the material (at temperatures below 20°C) and "hot" (above 20°C). When specifying a linear dependence according to the equation λ = a + b*t or an exponential one according to the equation λ = a*exp(b*t), the coefficients "a" and "b" are specified in the fields, respectively, "Const(cold) a" and "Const(cold) b", or "Const(hot) a" and "Const(hot) b". A constant value (when selecting a constant as the dependence type) is specified in the "Const(cold) a" or "Const(hot) a" field. When selecting dependencies by reference points (parabolic, spline, etc.), the points of the thermal conductivity dependence on temperature are specified in the corresponding table, where the temperature is in °C, the thermal conductivity coefficient is in W /(m*K), "cold applic." is an indicator of the temperature range to which the given point belongs (if the checkbox opposite the point is checked, then it belongs to the "cold" one, if not, then it belongs to the "hot" one). The number of points in the table for each of the ranges must correspond to the dependence selected for the given range (2 in the case of linear, 3 in the case of parabolic, 3 or more in the case of spline and broken-line dependence), otherwise the approximation of these points by the equation may be performed incorrectly. To edit a value already entered in the table, double-click on this value; to delete a point from the table, select it and press "Delete" on the keyboard. When specifying thermal conductivity (and other parameters in materials database) a dot (not a comma) must be used as a separator between the integer and fractional parts;
standard sizes (thickness, length, etc.) of the material - required only for some types of materials, such as mats, cylinders, etc. The columns "Size1", "Size2" and "Size3" are interpreted differently for different types of materials - hover the cursor over the column designation with the corresponding size and the status line (bottom left) will indicate what is meant by this size for different types of materials.
If at least one of the above characteristics is not filled in, the material cannot be used in calculations - it will simply not be available in the list of available materials when specifying a thermal insulation for a pipeline. Please note that all other (not mentioned above) characteristics of materials are not required for heat calculation (they're required for other calculations in other PASS software), so they can
After editing/entering insulation materials, save the changes to the database, after which the modified information on materials will be available for thermal calculation of the pipeline.