Learn about PASS/START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
Model equal-leg angular valves using standard valve element. Place at node between connecting pipes. Valve length divides equally along both pipe directions. Supports different pipe diameters.

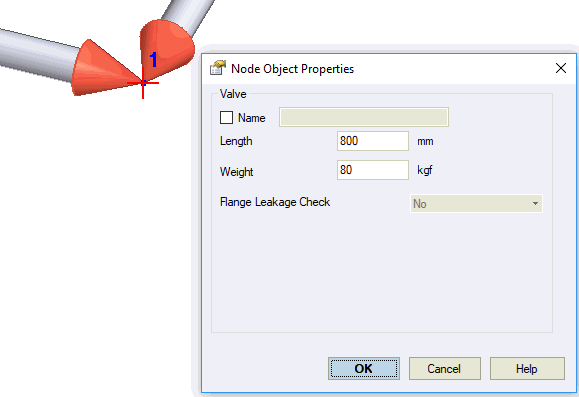
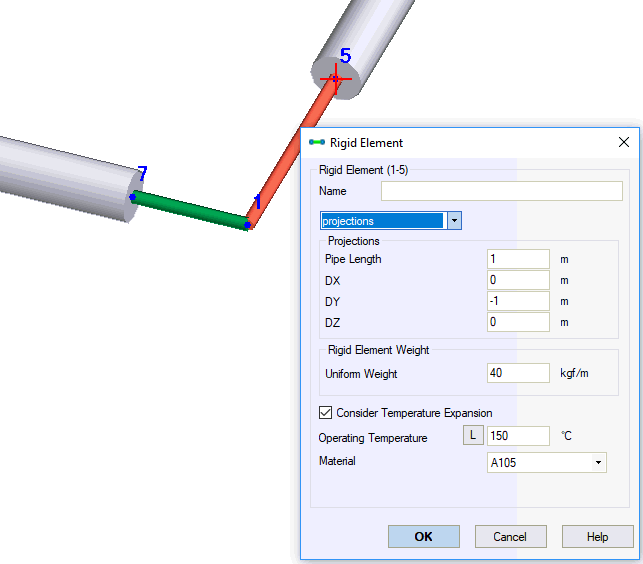
Model unequal-leg valves using rigid elements. Set total rigid element weight equal to valve weight. Specify temperature and material in rigid elements for thermal expansion. Add flanges at valve ends for leakage analysis.
Model three-way valves using three rigid elements.

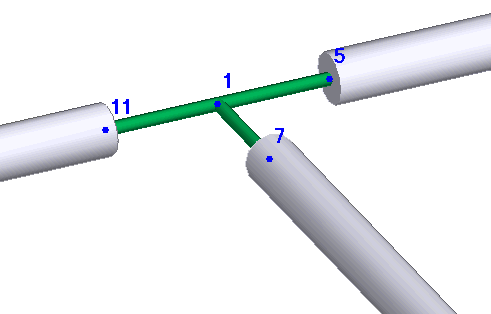
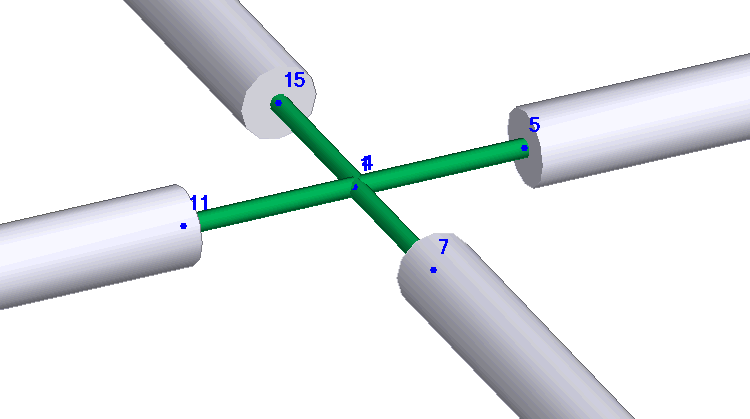
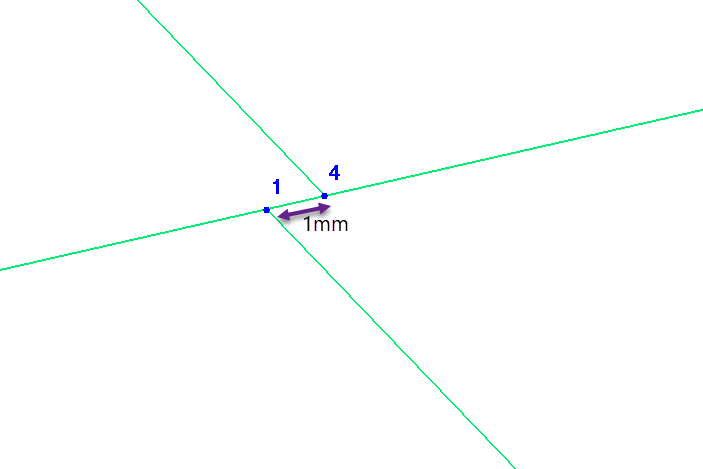
PASS/START-PROF prohibits four elements at one node. Model crosses by offsetting one connecting element node by 1mm. Model four-way valves using four rigid elements. Set total rigid element weight equal to valve weight.
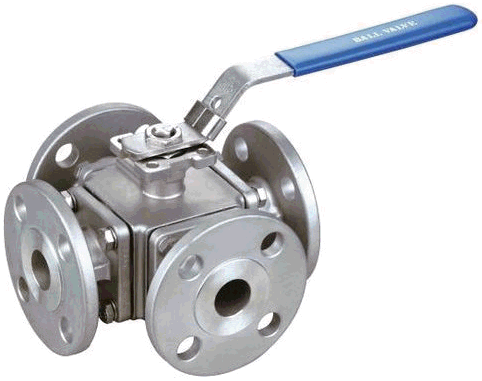
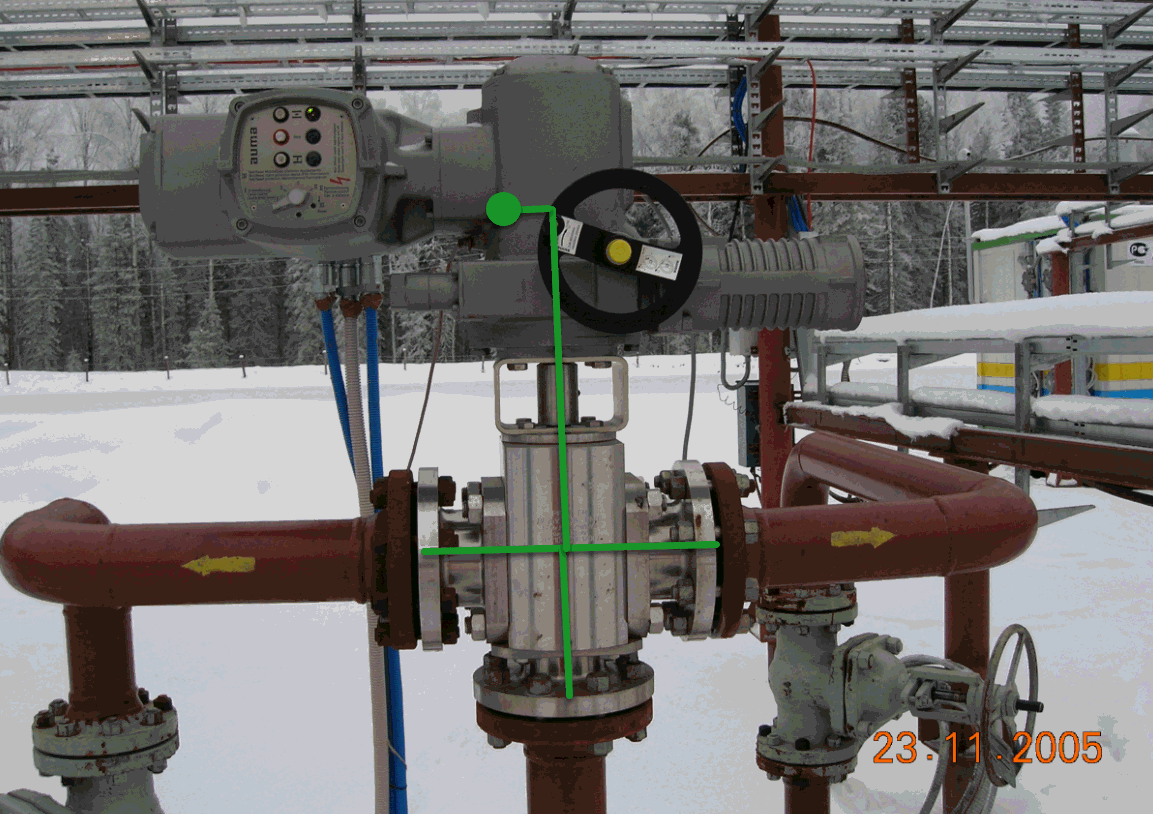
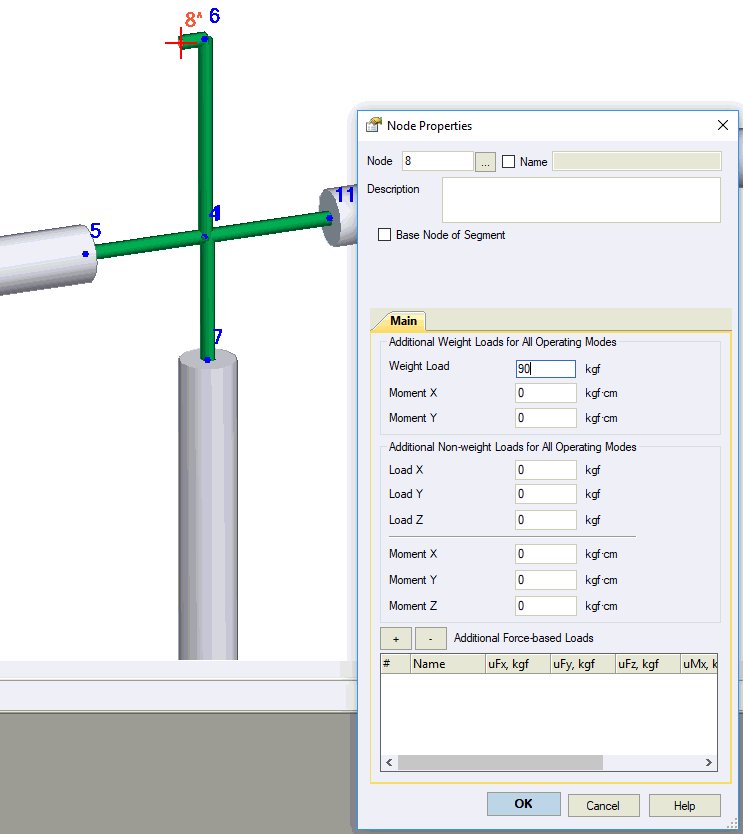
Model heavy wheels or actuators as nodal weight at center of gravity. Connect to valve using zero-weight rigid elements to account for eccentricity. Proper eccentricity modeling is critical for seismic analysis to capture additional torsion and bending moments.