Running
calculation
The
following types of calculations are provided in the Hydrosystem:
isothermal
flow calculation - hydraulic calculation of steady-state
(stationary) flow with constant temperature in a pipeline with a fully
known configuration. In this calculation thermal effects (heat exchange
with the environment, various internal cooling/warming effects in
the fluid, etc.) are not taken into account, the fluid temperature
in the pipeline is taken to be equal to the values specified in the
input data. To run this calculation, click the  button of the Main
toolbar and select the "Calculate Isothermal Flow"
sub-item
button of the Main
toolbar and select the "Calculate Isothermal Flow"
sub-item  (or use the
corresponding "Analysis" menu item);
(or use the
corresponding "Analysis" menu item);
diameters
calculation - hydraulic calculation of steady-state (stationary)
flow for a pipeline with unknown or partially known diameters (and
with the aim to determine them). In this calculation thermal effects
(heat exchange with the environment, various internal cooling/warming
effects in the fluid, etc.) are not taken into account, the fluid
temperature in the pipeline is taken to be equal to the values specified
in the input data. To run this calculation, click the  button of the Main
toolbar and select the "Calculate Diameters" sub-item
button of the Main
toolbar and select the "Calculate Diameters" sub-item  (or use the corresponding "Analysis" menu item).
Please note that upon completion of the diameters calculation, if
the diameters are successfully calculated, the following message will
be displayed:
(or use the corresponding "Analysis" menu item).
Please note that upon completion of the diameters calculation, if
the diameters are successfully calculated, the following message will
be displayed:
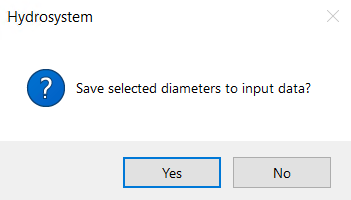
If you click "Yes"
in this window, the selected values of the internal diameters will be
saved in the input data for the branches. This is convenient in cases
where other calculations are planned for this pipeline, for example, the
control valves sizing or the calculation of waterhammer, since for these
calculations the diameters must be specified in the initial data. However,
this may be inconvenient in cases where it is necessary to repeat the
diameters calculation for this pipeline (for example, with other initial
data or other calculation settings) - if the diameter is specified in
the initial data, it will be considered a known value during the calculation
and its value will not be calculated. Therefore, for such cases, it is
better to click "No" in the above window. The selected diameters
in this case will be shown in the calculation results, but will not be
stored in the initial data.
Note: If you accidentally
saved the diameters in the input data by clicking "Yes" in this
window, you can cancel this operation by clicking the  button of the Edit toolbar or using
the corresponding "Edit" menu item. In addition, you can quickly
"zero out" the selected diameters in all branches using group
replacement operations (for more information, see here);
button of the Edit toolbar or using
the corresponding "Edit" menu item. In addition, you can quickly
"zero out" the selected diameters in all branches using group
replacement operations (for more information, see here);
heat and
hydraulic calculation - thermal and hydraulic calculation
of steady-state (stationary) flow in a pipeline with a fully known
configuration. This calculation takes into account the thermal interaction
of the pipeline with the environment, heat gain due to internal friction
in the fluid, inversion and other thermal effects in the pumped fluid,
as a result of which, in addition to the hydraulic calculation, the
change in the fluid temperature along the flow is also calculated.
To run this calculation, click  button
of the Main toolbar and
select the "Calculate Heat and Hydraulic" sub-item
button
of the Main toolbar and
select the "Calculate Heat and Hydraulic" sub-item  (or use the corresponding "Analysis" menu
item);
(or use the corresponding "Analysis" menu
item);
Please
note that some calculations may be unavailable, for example, if you do
not have licensed certain program modules or if the calculation is performed
for a two-phase flow with mass transfer (with the "Undefined"
fluid phase state) for which isothermal and diameters calculations are
not provided. Calculations of steady-state flow (isothermal flow analysis,
diameters calculation and heat and hydraulic calculation) can be performed
either for each pipeline in the project separately (by selecting this
pipeline or any of its elements in the project tree), or for all pipelines
in the project (if there are several) simultaneously. In the latter case,
you need to select the project in the tree before running the calculation.
If errors are detected in the input
data or during the calculation process, they will be shown in the calculation
log window. Error messages in the calculation log are synchronized with
the project tree and the Object Properties Window. When you click a specific
message, the object to which this message refers is selected in these
windows - this way you can easily find out what caused the problem in
the calculation, then change the input data and run the calculation again. In addition to the above-mentioned
window, the isothermal flow calculation log is also saved in the 'hydro.log'
file, which is written to the temporary files directory of the Windows
user account. Additional information (maximum error in calculating flow
rates and pressures and the number of iterations in the calculation) is
also output to this file.
If
any changes are made to the input data, the calculation results are immediately
reset. Also, the results of the calculations performed are not saved together
with the project file, so when opening a previously saved file to view
the calculation results in it, it is necessary to repeat the calculation
for pipelines.
 button of the Main
toolbar and select the "Calculate Isothermal Flow"
sub-item
button of the Main
toolbar and select the "Calculate Isothermal Flow"
sub-item  (or use the
corresponding "Analysis" menu item);
(or use the
corresponding "Analysis" menu item); (or use the corresponding "Analysis" menu item).
Please note that upon completion of the diameters calculation, if
the diameters are successfully calculated, the following message will
be displayed:
(or use the corresponding "Analysis" menu item).
Please note that upon completion of the diameters calculation, if
the diameters are successfully calculated, the following message will
be displayed:

 (or use the corresponding "Analysis" menu
item);
(or use the corresponding "Analysis" menu
item); button of the
button of the
 button
of the
button
of the  button
of the
button
of the