 button
of the Components
toolbar (or use the corresponding Insert
menu item). Next, in the Object Properties Window for the added component,
you will need to select a substance (or pseudo-substance) and set its
percentage content.
button
of the Components
toolbar (or use the corresponding Insert
menu item). Next, in the Object Properties Window for the added component,
you will need to select a substance (or pseudo-substance) and set its
percentage content.Properties library
This library is designed for calculating the properties of various pure substances and their mixtures with each other. When using the "Properties" library, it is necessary to enter the molar or mass composition of the fluid (which is set using the corresponding switch in the Object Properties Window for the fluid); the composition is specified component by component.
To add a fluid component, select
the fluid (or any already existing component of this fluid) in the project
tree and click the  button
of the Components
toolbar (or use the corresponding Insert
menu item). Next, in the Object Properties Window for the added component,
you will need to select a substance (or pseudo-substance) and set its
percentage content.
button
of the Components
toolbar (or use the corresponding Insert
menu item). Next, in the Object Properties Window for the added component,
you will need to select a substance (or pseudo-substance) and set its
percentage content.
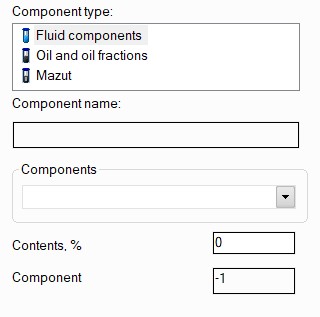
In the "Properties" library, all substances and fluids are grouped into three categories:
fluid components - "ordinary" chemical substances and compounds;
oil and oil fractions - this category includes various oils, petroleum, gasoline, kerosene, fuels, etc.;
mazuts a.k.a. black oils
You must specify the component type and then select the component name from the drop-down list. Substances can be "searched by first letters": to do this, place the cursor in the drop-down list and start entering its name. As you type, the list will scroll to the first component that matches the name. After selecting a component, its code will be displayed in the corresponding field, which, if necessary, allows you then to switch the method for calculating fluid properties to some other library without re-entering the components (of course, only if this library contains all the components entered).
Then, in the corresponding field, you must enter the percentage of the selected component in the mixture. Please note that if mazut is selected, the content is not specified - it is assumed that, if selected, the mazut is the only component of the fluid and the fluid should not contain any other media/substances (therefore, when specifying mazut, the ability to add any other components to the fluid is blocked). The full list of substances and media available in the "Properties" library (about 200) can be found here.
Please note that the "Properties" library can only calculate the thermophysical properties of fluids. Phase equilibria are not calculated using this library, so it cannot be used when specifying an "Undefined" phase state of the fluid (for which phase equilibrium calculations are required), and this library does not check the phase state or diagnose possible phase transitions of the fluid. In addition, the "Properties" library should be used with caution if you plan to calculate waterhammer. For this type of calculation, in some cases, the value of the isothermal speed of sound (on which the shock wave speed and, as a consequence, the force of the waterhammer depend) is important, which the "Properties" library does not allow calculating for liquids. In this case, a certain average value of the speed of sound (1000 m/s) will be used in the calculation.
Information on methods for calculating the properties of substances and their mixtures in the "Properties" library can be found here.