Learn more about PASS/START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
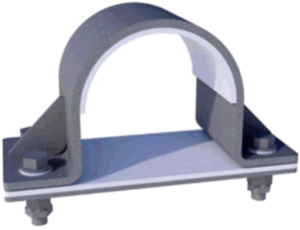
For clamps that restrict horizontal and vertical movement without applying downward force, use a double-acting guide support.
The axial friction force F is calculated as:
F = Rym · μ + Rzm · μ
Where:
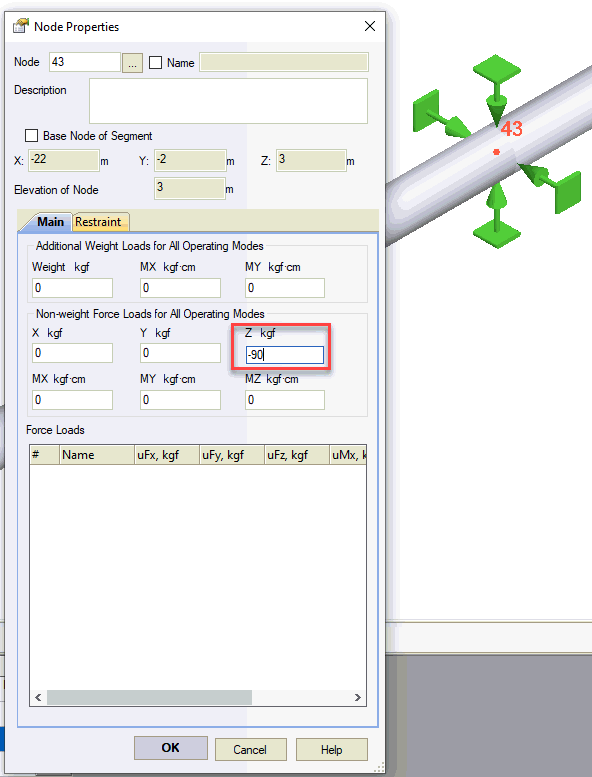
For clamps with tightening force that creates additional downward pressure, include the preload force Fp in the double-acting guide support model.
The axial friction force F becomes:
F = Rym · μ + Rzm · μ + Fp · μ