Service life analysis methods apply to steel industrial pipelines and industrial furnace coils analyzed per GOST 32388-2013. Piping service life equals the minimum service life of its elements and joints. Service life defines the operating period (years, thousands of hours) after which piping operation must stop for remaining strength analysis. Input service life must not exceed 20 years.
For moderate temperature piping elements in fatigue analysis, service life calculates as:
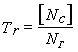 (1)
(1)
Where NГ - total load cycles per year of operation, [Nc] - allowable load cycles for pipe element
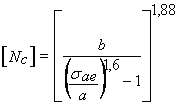
Where a = 80 MPa and b = 1200 - for carbon and permitted non-austenitic steel elements; a = 110 MPa and b = 1000 - for austenitic steel elements.
For high-temperature pipelines and coils in fatigue analysis, service life calculates as:
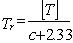 when
c > 1.0 (2)
when
c > 1.0 (2)
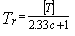 when
c ≤ 1.0
when
c ≤ 1.0
Where:
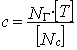
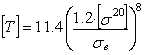
Without stress analysis and corrosion wear, [T] calculates as:
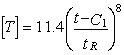
Note: Factor 11.4 corresponds to 100 thousand hours. For medium-temperature pipelines with wall corrosion-erosion, service life calculates as:
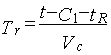 (3)
(3)
For high-temperature pipelines and coils with corrosion and static load:
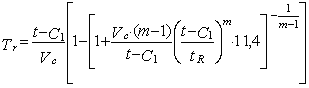 (4)
(4)
Where Vc - corrosion rate in mm/year, t, tR - nominal and design element wall thickness, С1 - wall mill allowance, m - time dependence exponent for long-term tensile strength (use 8 without reference data).
For medium-temperature pipelines with material fatigue damage and corrosion-erosion wear, use formulas (1) and (3), selecting the lower value.
For high-temperature pipelines with material fatigue damage and corrosion-erosion wear, use formulas (2) and (4), selecting the lower value.
When design wall thickness falls below minimum allowable for medium- and high-temperature pipelines, use formulas (3) and (4) with design thickness replaced by minimum allowable, selecting the lower value.
When wear rate decreases significantly during initial operation with sufficient experimental data, wall thickness mill-through time expresses as:
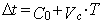
For service life calculations using formulas (3)-(4), substitute С1+Со for С1.