Learn about START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
As temperature decreases, most materials exhibit increased strength properties including tensile strength, yield stress, and fatigue limit. The modulus of elasticity typically increases while plasticity decreases, reflected in reduced relative elongation and impact strength. The coefficient of linear thermal expansion also decreases.
Cold brittleness describes the tendency of some materials to transition to brittle fracture at low temperatures without significant plastic deformation.
Different materials demonstrate varying mechanical property changes with temperature reduction. For service temperatures below -70°C, the most commonly used materials are 300 series stainless steels in the USA and chromium-nickel austenitic steels such as 12X18H10T in Russia. These alloys contain 16-22% chromium and 8-14% nickel.
The key characteristics of these steels include excellent corrosion resistance along with maintained toughness and ductility at cryogenic temperatures. Unlike carbon and low-alloy steels, austenitic stainless steels experience minimal reduction in plastic properties as temperatures decrease. Their thermoplastic properties ensure reliable piping system operation down to -269°C.
Non-ferrous metals and alloys are also widely used in low and ultra-low temperature applications due to their ability to maintain ductility in cryogenic service.
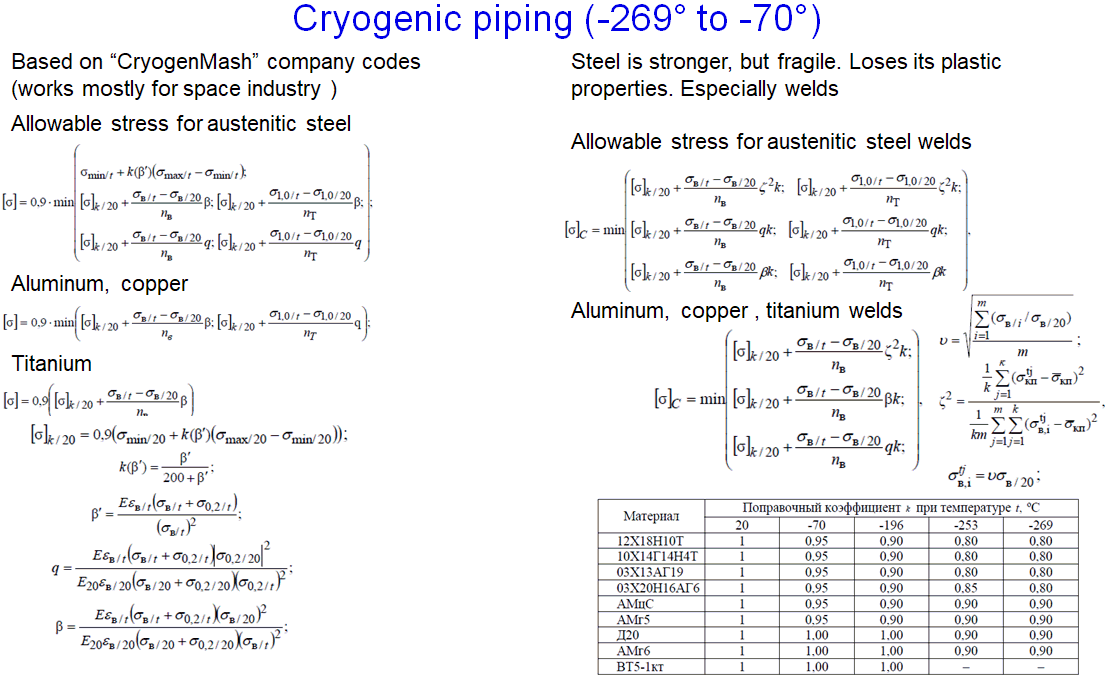
Cryogenic piping analysis can be performed using ASME B31.3, EN 13480, and GOST 32388 codes. While ASME B31.3 and EN 13480 contain no specific cryogenic piping analysis methods, GOST 32388 includes a dedicated chapter for cryogenic piping stress analysis.
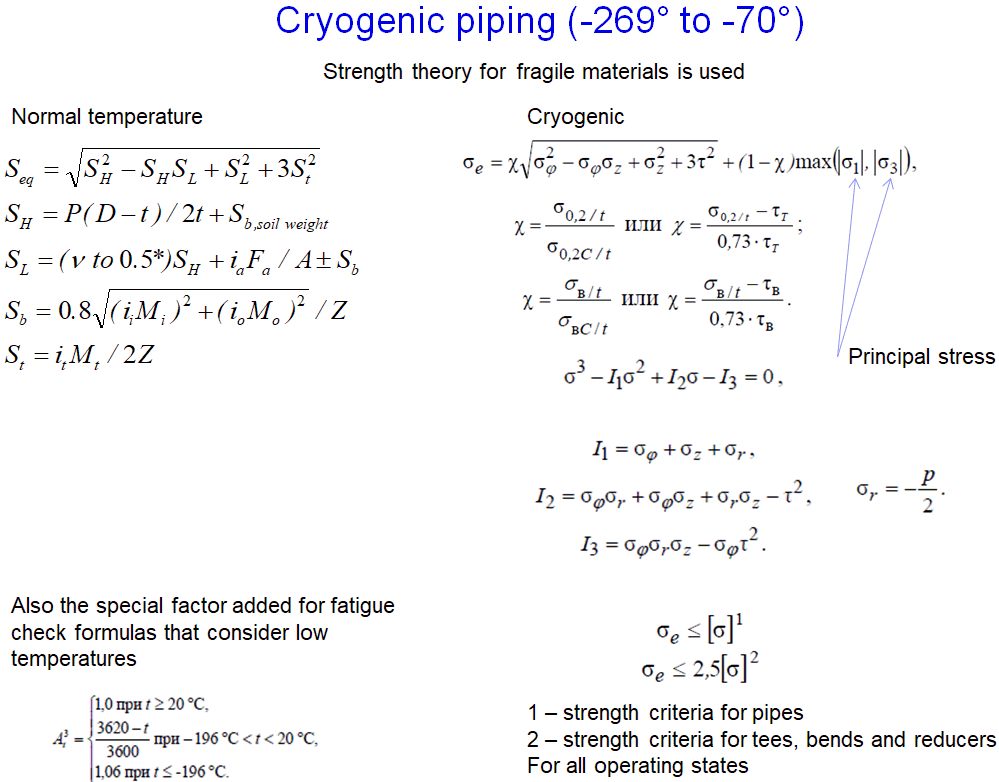
The GOST 32388-2013 cryogenic piping stress analysis procedure differs from conventional temperature piping analysis. Beyond using material properties at low temperatures (allowable stress, modulus of elasticity, thermal expansion coefficient), the stress calculation formulas also change. The methodology incorporates plasticity factors and simultaneously applies both the first and fourth strength theories (Von Mises):
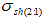
Additionally, strength conditions vary across different operating modes for cryogenic service.