Learn more about PASS/START-PROF pipe stress analysis software
Analyzing buried piping with resting supports, guides, and other restraints presents an indeterminate problem. Support loads are highly sensitive to installation tolerances.
Typical applications include:
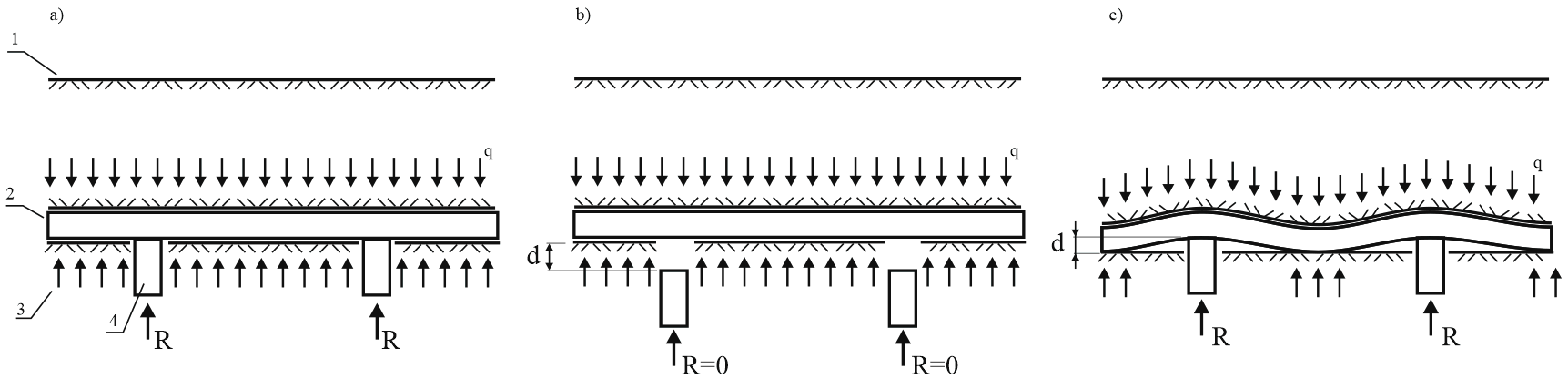
The diagram below illustrates three installation scenarios:
Scenario A: Supports installed flush with trench bottom. Support loads remain zero as soil bears the pipe weight.
Scenario B: Supports installed below trench bottom. Support loads remain zero as trench bottom soil carries all pipe and backfill weight.
Scenario C: Supports installed above trench bottom. Support loads become significant as they carry the entire pipe and backfill weight.
Modeling resting supports (piles) on buried piping
A - Piles flush with trench bottom, B - Piles below trench bottom, C - Piles above trench bottom
1 - Ground surface, 2 - Pipe, 3 - Trench bottom soil reaction, 4 - Support (pile), q - Backfill soil weight, R - Pile reaction force
Actual support loads depend critically on installation accuracy. Minor vertical displacements create substantial load variations, making precise prediction impossible.
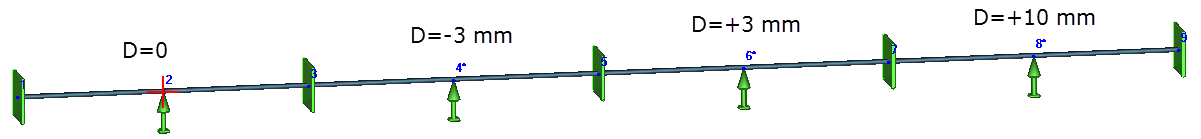
The following example demonstrates this sensitivity. A buried pipeline with four supports shows varying reactions based on installation positions: